Autophagy: a forty-year search for a missing membrane source
- PMID: 16464128
- PMCID: PMC1363699
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040036
Autophagy: a forty-year search for a missing membrane source
Abstract
Autophagy is central to diverse biological processes in eukaryotes including animal development and cellular survival, and also to neurodegenerative diseases, but the origin of the membranes that make up autophagic vesicles is unknown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
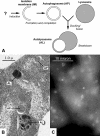
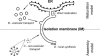
References
-
- De Duve C, Wattiaux R. Functions of lysosomes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1966;28:435–492. - PubMed
-
- Levine B, Klionsky DJ. Development by self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell. 2004;6:463–477. - PubMed
-
- Bellu AR, Kiel JA. Selective degradation of peroxisomes in yeasts. Microsc Res Tech. 2003;61:161–170. - PubMed
-
- Rusten TE, Lindmo K, Juhasz G, Sass M, Seglen PO, et al. Programmed autophagy in the Drosophila fat body is induced by ecdysone through regulation of the PI3K pathway. Dev Cell. 2004;7:179–192. - PubMed
-
- Scott RC, Schuldiner O, Neufeld TP. Role and regulation of starvation-induced autophagy in the Drosophila fat body. Dev Cell. 2004;7:167–178. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

