Persistent increase in the incidence of acute male urethritis diagnosed in general practices in France
- PMID: 16464324
- PMCID: PMC1828216
Persistent increase in the incidence of acute male urethritis diagnosed in general practices in France
Abstract
Background: At-risk sexual behaviour seems to have increased in Europe, possibly due to the reassuring efficacy of highly active antiretroviral treatments.
Aim: To follow, from 1990 to 2003, in France, the trends in the incidence of acute male urethritis diagnosed in general practice, a marker of at-risk sexual behaviour.
Design of study: Electronic disease surveillance.
Setting: General practices located all over mainland France.
Method: The GPs of the French Sentinelles network reported, via online computer systems, the acute urethritis cases they diagnosed, and for each case the characteristics of the patients.
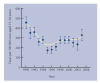
Results: After a striking decrease between 1990 and 1995 from 460 per 100 000 men aged 15-64 years (95% confidence interval [CI] = 390 to 520) to 180 (95% CI = 150 to 200), when antiretroviral drugs became available on the French market, the incidence of acute male urethritis stopped decreasing. Between 1996 and 2003, it may have risen again from 190 per 100 000 men (95% CI = 160 to 210) to 325 per 100 000 men (95% CI = 280 to 370) aged 15-64 years. The percentage of homosexual/bisexual men among the cases reported was higher than in the general population (10% versus 4%, P<0.001). Homosexual/bisexual patients were younger than heterosexual patients (34 versus 37 years, P = 0.04), more of them had a discharge (88% versus 59%, P<0.001), a history of sexually transmitted disease (65% versus 32%, P<0.001), and at least two sexual partners (74% versus 38%, P<0.001). The most frequent pathogens were Chlamydia trachomatis (25%), Neisseria gonorrhoea (21%), Mycoplasma genitalium (8%), Ureaplasma urealyticum (5%), Trichomonas vaginalis (3%) and other bacteria (32%). Presence of co-infections was observed in 8.3% of patients.
Conclusions: This increase in the incidence of urethritis, shows that the sexual health of men has worsened in France, and calls for urgent new preventive measures.
Figures
References
-
- HIV/AIDS Surveillance in Europe. End-year report 2003, no 70. http://www.eurohiv.org/reports/index_reports_eng.htm (accessed 16 Dec 2005)
-
- Miller M, Meyer L, Boufassa F, et al. Sexual behavior changes and protease inhibitor therapy SEROCO Study Group. AIDS. 2000;14:F33–F39. - PubMed
-
- Adam P, Hauet E, Caron C, et al. Sur la recrudescence des prises de risques et des MST parmi les gays. Rapport préliminaire de l'enquête presse Gay 2000. Saint-Maurice: Institut de veille sanitaire; 2001.
-
- Martin IM, Ison CA. Rise in gonorrhoea in London, UK. London Gonoccocal Working Group. Lancet. 2000;355:623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials