Loss-of-function mutations in the keratin 5 gene lead to Dowling-Degos disease
- PMID: 16465624
- PMCID: PMC1380294
- DOI: 10.1086/500850
Loss-of-function mutations in the keratin 5 gene lead to Dowling-Degos disease
Abstract
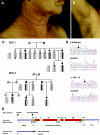
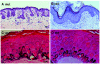
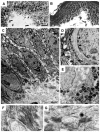
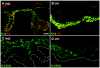
Dowling-Degos disease (DDD) is an autosomal dominant genodermatosis characterized by progressive and disfiguring reticulate hyperpigmentation of the flexures. We performed a genomewide linkage analysis of two German families and mapped DDD to chromosome 12q, with a total LOD score of 4.42 ( theta =0.0) for marker D12S368. This region includes the keratin gene cluster, which we screened for mutations. We identified loss-of-function mutations in the keratin 5 gene (KRT5) in all affected family members and in six unrelated patients with DDD. These represent the first identified mutations that lead to haploinsufficiency in a keratin gene. The identification of loss-of-function mutations, along with the results from additional functional studies, suggest a crucial role for keratins in the organization of cell adhesion, melanosome uptake, organelle transport, and nuclear anchorage.
Figures
References
Web Resources
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for KRT5 [accession numbers NM_000424 and NP_000415])
-
- Human Intermediate Filament Mutation Database, http://www.interfil.org/ - PubMed
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.gov/Omim/ (for DDD) - PubMed
References
-
- Biltz H, Kiessling M (1988) Dowling-Degos disease: an autosomal dominant genetic dermatosis. Z Hautkr 63:642–644 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

