Human interleukin-15 improves engraftment of human T cells in NOD-SCID mice
- PMID: 16467330
- PMCID: PMC1391933
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.13.2.227-234.2006
Human interleukin-15 improves engraftment of human T cells in NOD-SCID mice
Abstract
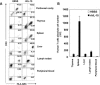
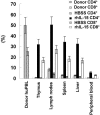
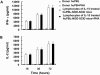
Human nonobese diabetic-severe combined immune deficiency (NOD-SCID) mouse chimeras have been widely used as an in vivo model to assess human immune function. However, only a small fraction of transferred human T lymphocytes can be detected in human peripheral blood lymphocyte (huPBL)-NOD-SCID chimeras. To improve the reconstitution of human T lymphocytes in NOD-SCID mice, the use of recombinant human interleukin-15 (rhIL-15) as a stimulator of human lymphocytes was explored. Administration of rhIL-15 after transplantation of huPBLs into NOD-SCID mice increased reconstitution of human T lymphocytes in a dose-dependent manner, with an optimal dosage of 1 microg/mouse. The number of human T lymphocytes (HLA-ABC+ CD3+) in the lymphoid organs or tissue of rhIL-15-treated huPBL-NOD-SCID mice increased 11- to 80-fold, and phytohemagglutinin-induced T-lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine production were significantly enhanced. Additionally, although mature human cells have not been thought to enter the murine thymus, human T lymphocytes were detected in the huPBL-NOD-SCID thymus after rhIL-15 treatment. Thus, rhIL-15 can be used to optimize long-term peripheral T-cell engraftment in these human-mouse chimeras and may also be useful in clinical treatment of T-cell deficiencies.
Figures




References
-
- Abedi, M. R., B. Christensson, K. B. Islam, L. Hammarstrom, and C. I. E. Smith. 1992. Immunoglobulin production in severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice reconstituted with human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 22:823-828. - PubMed
-
- Albert, S. E., C. Mckerlie, A. Pester, B.-J. Edgell, J. Carlyle, M. Petric, and J. W. Chamberlain. 1997. Time-dependent induction of protective antiinfluenza immune responses in human peripheral blood lymphocyte/SCID mice. J. Immunol. 159:1393-1403. - PubMed
-
- Baird, A. M., R. M. Gerstein, and L. J. Berg. 1999. The role of cytokine receptor signaling in lymphocyte development. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 11:157-166. - PubMed
-
- Barry, T. S., D. M. Jones, C. B. Richter, and B. F. Haynes. 1991. Successful engraftment of human postnatal thymus in severe combined immune deficient (SCID) mice: differential engraftment of thymic components with irradiation versus anti-asialo GM-1 immunosuppressive regimens. J. Exp. Med. 173:167-180. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernasconi, N. L., E. Traggiai, and A. Lanzavecchia. 2002. Maintenance of serological memory by polyclonal activation of human memory B cells. Science 298:2199-2202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

