Disinhibition opens the gate to pathological pain signaling in superficial neurokinin 1 receptor-expressing neurons in rat spinal cord
- PMID: 16467532
- PMCID: PMC6793628
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4584-05.2006
Disinhibition opens the gate to pathological pain signaling in superficial neurokinin 1 receptor-expressing neurons in rat spinal cord
Abstract
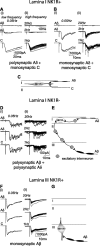
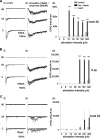
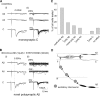
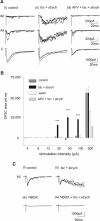
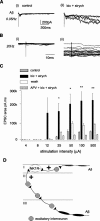
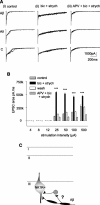
Blockade of local spinal cord inhibition mimics the behavioral hypersensitivity that manifests in chronic pain states. This suggests that there is a pathway capable of mediating allodynia/hyperalgesia that exists but is normally under strong inhibitory control. Lamina I and III neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor expressing (NK1R+) dorsal horn neurons, many of which are projection neurons, are required for the development of this hypersensitivity and are therefore likely to be a component of this proposed pathway. To investigate, whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were made from lamina I and III NK1R+ neurons in the spinal cord slice preparation with attached dorsal root. Excitatory postsynaptic currents were recorded in response to electrical stimulation of the dorsal root. Lamina I NK1R+ neurons were shown to receive high-threshold (Adelta/C fiber) monosynaptic input, whereas lamina III NK1R+ neurons received low-threshold (Abeta fiber) monosynaptic input. In contrast, lamina I neurons lacking NK1 receptor (NK1R-) received polysynaptic A fiber input. Blockade of local GABAergic and glycinergic inhibition with bicuculline (10 microm) and strychnine (300 nm), respectively, revealed significant A fiber input to lamina I NK1R+ neurons that was predominantly Abeta fiber mediated. This novel A fiber input was polysynaptic in nature and required NMDA receptor activity to be functional. In lamina I NK1R- and lamina III NK1R+ neurons, disinhibition enhanced control-evoked responses, and this was also NMDA receptor dependent. These disinhibition-induced changes, in particular the novel polysynaptic low-threshold input onto lamina I NK1R+ neurons, may be an underlying component of the hypersensitivity present in chronic pain states.
Figures
References
-
- Baba H, Ji RR, Kohno T, Moore KA, Ataka T, Wakai A, Okamoto M, Woolf CJ (2003). Removal of GABAergic inhibition facilitates polysynaptic A fiber-mediated excitatory transmission to the superficial spinal dorsal horn. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:818–830. - PubMed
-
- Bardoni R, Magherini PC, MacDermott AB (2000). Activation of NMDA receptors drives action potentials in superficial dorsal horn from neonatal rats. NeuroReport 11:1721–1727. - PubMed
-
- Bernard JF, Bester H, Besson JM (1996). Involvement of the spino-parabrachio-amygdaloid and -hypothalamic pathways in the autonomic and affective emotional aspects of pain. Prog Brain Res 107:243–255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
