Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel type 2 (SK2) modulates hippocampal learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 16467533
- PMCID: PMC6793641
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4106-05.2006
Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel type 2 (SK2) modulates hippocampal learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2006 Apr 26;26(17):4714
Abstract
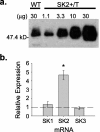
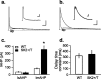
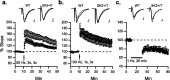
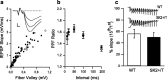
Apamin-sensitive, small-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channels (SK channels) modulate neuronal excitability in CA1 neurons. Blocking all SK channel subtypes with apamin facilitates the induction of hippocampal synaptic plasticity and enhances hippocampal learning. In CA1 dendrites, SK channels are activated by Ca2+ through NMDA receptors and restrict glutamate-mediated EPSPs. Studies of SK channel knock-out mice reveal that of the three apamin-sensitive SK channel subunits (SK1-SK3), only SK2 subunits are necessary for the apamin-sensitive currents in CA1 hippocampal neurons. To determine the specific influence of SK2 channels on hippocampal synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory, we used gene targeting through homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells to generate transgenic mice that overexpress SK2 subunits by 10-fold (SK2+/T). In these mice, the apamin-sensitive current in CA1 neurons was increased by approximately fourfold, relative to wild-type (WT) littermates. In addition, the amplitude of synaptically evoked EPSPs recorded from SK2+/T CA1 neurons increased twice as much in response to SK channel blockade relative to EPSPs recorded from WT CA1 neurons. Consistent with this, SK2 overexpression reduced long-term potentiation after high-frequency stimulation compared with WT littermates and severely impaired learning in both hippocampus- and amygdala-dependent tasks. We conclude that SK2 channels regulate hippocampal synaptic plasticity and play a critical role in modulating mechanisms of learning and memory.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Small conductance calcium-activated potassium type 2 channels regulate alcohol-associated plasticity of glutamatergic synapses.Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Apr 1;69(7):625-32. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.09.025. Epub 2010 Nov 5. Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21056409 Free PMC article.
-
Small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels modulate synaptic plasticity and memory encoding.J Neurosci. 2002 Dec 1;22(23):10163-71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-23-10163.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12451117 Free PMC article.
-
The small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel activator GW542573X impairs hippocampal memory in C57BL/6J mice.Neuropharmacology. 2024 Jul 1;252:109960. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.109960. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Neuropharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38631563 Free PMC article.
-
Small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels as targets of CNS drug development.Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004 Jun;3(3):161-7. doi: 10.2174/1568007043337472. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004. PMID: 15180477 Review.
-
Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels: form and function.Annu Rev Physiol. 2012;74:245-69. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-020911-153336. Epub 2011 Sep 19. Annu Rev Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21942705 Review.
Cited by
-
Elucidating the role of hypoxia/reoxygenation in hippocampus-dependent memory impairment: do SK channels play role?Exp Brain Res. 2021 Jun;239(6):1747-1763. doi: 10.1007/s00221-021-06095-8. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Exp Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33779792
-
Learning to learn - intrinsic plasticity as a metaplasticity mechanism for memory formation.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2013 Oct;105:186-99. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.07.008. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2013. PMID: 23871744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The sigma-1 receptor modulates NMDA receptor synaptic transmission and plasticity via SK channels in rat hippocampus.J Physiol. 2007 Jan 1;578(Pt 1):143-57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.116178. Epub 2006 Oct 26. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17068104 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Hippocampal Gamma Oscillations by Modulation of Intrinsic Neuronal Excitability.Front Neural Circuits. 2022 Jan 26;15:778022. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2021.778022. eCollection 2021. Front Neural Circuits. 2022. PMID: 35177966 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane caused learning and memory impairment via dysregulating SK2 channel endocytosis.Sci Prog. 2021 Jul-Sep;104(3):368504211043763. doi: 10.1177/00368504211043763. Sci Prog. 2021. PMID: 34533073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behnisch T, Reymann KG (1998). Inhibition of apamin-sensitive calcium dependent potassium channels facilitate the induction of long-term potentiation in the CA1 region of rat hippocampus in vitro. Neurosci Lett 253:91–94. - PubMed
-
- Blank T, Nijholt I, Kye MJ, Radulovic J, Spiess J (2003). Small-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channel SK3 generates age-related memory and LTP deficits. Nat Neurosci 6:911–912. - PubMed
-
- Bond CT, Sprengel R, Bissonnette JM, Kaufmann WA, Pribnow D, Neelands T, Storck T, Baetscher M, Jerecic J, Maylie J, Knaus HG, Seeburg PH, Adelman JP (2000). Respiration and parturition affected by conditional overexpression of the Ca2+-activated K+ channel subunit, SK3. Science 289:1942–1946. - PubMed
-
- Cai X, Liang CW, Muralidharan S, Kao JP, Tang CM, Thompson SM (2004). Unique roles of SK and Kv4.2 potassium channels in dendritic integration. Neuron 44:351–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
