Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel type 2 (SK2) modulates hippocampal learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 16467533
- PMCID: PMC6793641
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4106-05.2006
Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel type 2 (SK2) modulates hippocampal learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2006 Apr 26;26(17):4714
Abstract
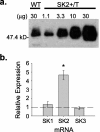
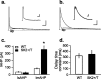
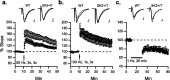
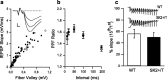
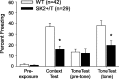
Apamin-sensitive, small-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channels (SK channels) modulate neuronal excitability in CA1 neurons. Blocking all SK channel subtypes with apamin facilitates the induction of hippocampal synaptic plasticity and enhances hippocampal learning. In CA1 dendrites, SK channels are activated by Ca2+ through NMDA receptors and restrict glutamate-mediated EPSPs. Studies of SK channel knock-out mice reveal that of the three apamin-sensitive SK channel subunits (SK1-SK3), only SK2 subunits are necessary for the apamin-sensitive currents in CA1 hippocampal neurons. To determine the specific influence of SK2 channels on hippocampal synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory, we used gene targeting through homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells to generate transgenic mice that overexpress SK2 subunits by 10-fold (SK2+/T). In these mice, the apamin-sensitive current in CA1 neurons was increased by approximately fourfold, relative to wild-type (WT) littermates. In addition, the amplitude of synaptically evoked EPSPs recorded from SK2+/T CA1 neurons increased twice as much in response to SK channel blockade relative to EPSPs recorded from WT CA1 neurons. Consistent with this, SK2 overexpression reduced long-term potentiation after high-frequency stimulation compared with WT littermates and severely impaired learning in both hippocampus- and amygdala-dependent tasks. We conclude that SK2 channels regulate hippocampal synaptic plasticity and play a critical role in modulating mechanisms of learning and memory.
Figures


References
-
- Behnisch T, Reymann KG (1998). Inhibition of apamin-sensitive calcium dependent potassium channels facilitate the induction of long-term potentiation in the CA1 region of rat hippocampus in vitro. Neurosci Lett 253:91–94. - PubMed
-
- Blank T, Nijholt I, Kye MJ, Radulovic J, Spiess J (2003). Small-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channel SK3 generates age-related memory and LTP deficits. Nat Neurosci 6:911–912. - PubMed
-
- Bond CT, Sprengel R, Bissonnette JM, Kaufmann WA, Pribnow D, Neelands T, Storck T, Baetscher M, Jerecic J, Maylie J, Knaus HG, Seeburg PH, Adelman JP (2000). Respiration and parturition affected by conditional overexpression of the Ca2+-activated K+ channel subunit, SK3. Science 289:1942–1946. - PubMed
-
- Cai X, Liang CW, Muralidharan S, Kao JP, Tang CM, Thompson SM (2004). Unique roles of SK and Kv4.2 potassium channels in dendritic integration. Neuron 44:351–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
