Site of action potential initiation in layer 5 pyramidal neurons
- PMID: 16467534
- PMCID: PMC6793621
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4812-05.2006
Site of action potential initiation in layer 5 pyramidal neurons
Abstract
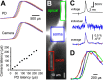
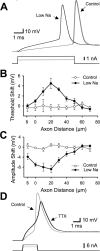
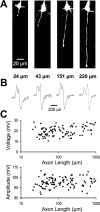
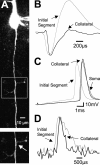
Fundamental to an understanding of how neurons integrate synaptic input is the knowledge of where within a neuron this information is converted into an output signal, the action potential. Although it has been known for some time that action potential initiation occurs within the axon of neurons, the precise location has remained elusive. Here, we provide direct evidence using voltage-sensitive dyes that the site of action potential initiation in cortical layer 5 pyramidal neurons is approximately 35 microm from the axon hillock. This was the case during action potential generation under a variety of conditions, after axonal inhibition, and at different stages of development. Once initiated action potentials propagated down the axon in a saltatory manner. Experiments using local application of low-sodium solution and TTX, as well as an investigation of the influence of axonal length on action potential properties, provided evidence that the initial 40 microm of the axon is essential for action potential generation. To morphologically identify the relationship between the site of action potential initiation and axonal myelination, we labeled oligodendrocytes supplying processes to the proximal region of the axon. These experiments indicated that the axon initial segment was approximately 40 mcirom in length, and the first node of Ranvier was approximately 90 microm from the axon hillock. Experiments targeting the first node of Ranvier suggested it was not involved in action potential initiation. In conclusion, these results indicate that, in layer 5 pyramidal neurons, action potentials are generated in the distal region of the axon initial segment.
Figures



References
-
- Bishop PO, Levick WR (1956). Saltatory conduction in single isolated and non-isolated myelinated nerve fibres. J Cell Physiol 48:1–34. - PubMed
-
- Boiko T, Rasband MN, Levinson SR, Caldwell JH, Mandel G, Trimmer JS, Matthews G (2001). Compact myelin dictates the differential targeting of two sodium channel isoforms in the same axon. Neuron 30:91–104. - PubMed
-
- Buhl EH, Han ZS, Lorinczi Z, Stezhka VV, Karnup SV, Somogyi P (1994). Physiological properties of anatomically identified axo-axonic cells in the rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 71:1289–1307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
