Osteoprotegrin knockout mice demonstrate abnormal remodeling of the otic capsule and progressive hearing loss
- PMID: 16467704
- PMCID: PMC2563156
- DOI: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000191466.09210.9a
Osteoprotegrin knockout mice demonstrate abnormal remodeling of the otic capsule and progressive hearing loss
Abstract
Objectives: The otic capsule, when compared with other bones in the body, is unique in that it undergoes no significant remodeling of bone after development. We previously demonstrated that osteoprotegerin (OPG), which inhibits formation and function of osteoclasts, is produced at high levels in the inner ear of normal mice and secreted into the perilymph from where it diffuses into the surrounding otic capsule bone through a lacunocanalicular system. To test our hypothesis that the high level of OPG may be important in the inhibition of otic capsule remodeling, we studied the light microscopic histology of the otic capsule in OPG knockout mice for evidence of abnormal remodeling of bone. We also tested the hearing in OPG knockout mice to determine whether OPG and its influence on surrounding bone is important for auditory function.
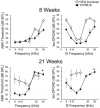
Methods: Temporal bone histopathology and pathophysiology were compared in homozygous OPG knockout mice and C57BL/6 (B6) mice, the background strain for the knockouts. Auditory function in age-matched animals from each group was evaluated at approximately 4-week intervals from 8 to 21 weeks using frequency-specific auditory brainstem responses (ABR) and distortion product otoacoustic emissions (DPOAE). After each of the last three evaluations, the cochleae from one mouse of each group were harvested, processed, and examined by light microscopy.
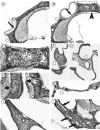
Results: Osteoprotegerin knockout mice demonstrated abnormal remodeling of bone within the otic capsule with multiple foci showing osteoclastic bone resorption and formation of new bone. Such changes were not seen in the age-matched B6 controls. The active bone remodeling process in the knockout animals showed many similarities to otosclerosis seen in human temporal bones. Over the time period that we monitored, auditory function was significantly and progressively compromised in the knockout animals relative to B6 controls. At the earliest age of test (8 wk), the loss was apparent as a mild, high-frequency reduction in sensitivity by ABR. In contrast, DPOAE losses in the knockouts were substantial even at 8 weeks, and by 21 weeks, these losses exceeded our equipment limits. Results of ABR testing showed hearing sensitivity changes in the animals of the background strain were confined largely to the high frequencies, whereas OPG knockouts demonstrated substantial low-frequency shifts in addition to those at high frequencies.
Conclusions: The histopathological and pathophysiological findings in OPG knockout mice support the hypothesis that OPG is important in the inhibition of bone remodeling within the otic capsule and the maintenance of normal auditory function. This mouse may provide a valuable animal model of human otosclerosis.
Figures
References
-
- Frisch T, Sorensen MS, Overgaard S, et al. Estimation of volume referent bone turnover in the otic capsule after sequential point labeling. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2000;109:33–39. - PubMed
-
- Hofbauer LC, Neubauer A, Heufelder AE. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin: potential implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of malignant bone diseases. Cancer. 2001;92:460–470. - PubMed
-
- Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Yasuda H, et al. Osteoprotegerin produced by osteoblasts is an important regulator in osteoclast development and function. Endocrinology. 2000;141:3478–3484. - PubMed
-
- Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, et al. Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell. 1997;89:309–319. - PubMed
-
- Zehnder AF, Kristiansen AG, Adams JC, et al. Osteoprotegerin in the inner ear may inhibit bone remodeling in the otic capsule. Laryngoscope. 2005;115:172–177. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

