A hyper-dynamic equilibrium between promoter-bound and nucleoplasmic dimers controls NF-kappaB-dependent gene activity
- PMID: 16467852
- PMCID: PMC1383558
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600977
A hyper-dynamic equilibrium between promoter-bound and nucleoplasmic dimers controls NF-kappaB-dependent gene activity
Abstract
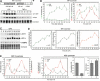
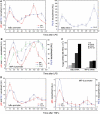
Because of its very high affinity for DNA, NF-kappaB is believed to make long-lasting contacts with cognate sites and to be essential for the nucleation of very stable enhanceosomes. However, the kinetic properties of NF-kappaB interaction with cognate sites in vivo are unknown. Here, we show that in living cells NF-kappaB is immobilized onto high-affinity binding sites only transiently, and that complete NF-kappaB turnover on active chromatin occurs in less than 30 s. Therefore, promoter-bound NF-kappaB is in dynamic equilibrium with nucleoplasmic dimers; promoter occupancy and transcriptional activity oscillate synchronously with nucleoplasmic NF-kappaB and independently of promoter occupancy by other sequence-specific transcription factors. These data indicate that changes in the nuclear concentration of NF-kappaB directly impact on promoter function and that promoters sample nucleoplasmic levels of NF-kappaB over a timescale of seconds, thus rapidly re-tuning their activity. We propose a revision of the enhanceosome concept in this dynamic framework.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

