Neuromusculoskeletal modeling: estimation of muscle forces and joint moments and movements from measurements of neural command
- PMID: 16467928
- PMCID: PMC1357215
- DOI: 10.1123/jab.20.4.367
Neuromusculoskeletal modeling: estimation of muscle forces and joint moments and movements from measurements of neural command
Abstract
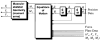
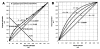
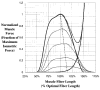
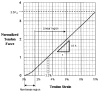
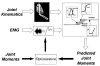
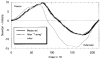
This paper provides an overview of forward dynamic neuromusculoskeletal modeling. The aim of such models is to estimate or predict muscle forces, joint moments, and/or joint kinematics from neural signals. This is a four-step process. In the first step, muscle activation dynamics govern the transformation from the neural signal to a measure of muscle activation-a time varying parameter between 0 and 1. In the second step, muscle contraction dynamics characterize how muscle activations are transformed into muscle forces. The third step requires a model of the musculoskeletal geometry to transform muscle forces to joint moments. Finally, the equations of motion allow joint moments to be transformed into joint movements. Each step involves complex nonlinear relationships. The focus of this paper is on the details involved in the first two steps, since these are the most challenging to the biomechanician. The global process is then explained through applications to the study of predicting isometric elbow moments and dynamic knee kinetics.
Figures
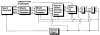
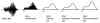

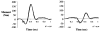
References
-
- An KN, Takahashi K, Harrigan TP, Chao EY. Determination of muscle orientations and moment arms. Journal of Biomechical Engineering. 1984;106:280–282. - PubMed
-
- Anderson FC, Pandy MG. Dynamic optimization of human walking. Journal of Biomechical Engineering. 2001;123:381–390. - PubMed
-
- Bouisset, S. (1973). EMG and muscle force in normal motor activities Basel: Karger.
-
- Buchanan TS. Evidence that maximum muscle stress is not a constant: Differences in specific tension in elbow flexors and extensors. Medical Engineering and Physics. 1995;17:529–536. - PubMed
-
- Buchanan TS, Almdale DPJ, Lewis JL, Rymer, WZ Characteristics of synergic relations during isometric contractions of human elbow muscles. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1986;5:1225–1241. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

