Vegetable acceptance by infants: effects of formula flavors
- PMID: 16469455
- PMCID: PMC2366040
- DOI: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2005.12.001
Vegetable acceptance by infants: effects of formula flavors
Abstract
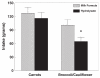
Individual differences in acceptance patterns are evident as early as the child's first experiences with a particular food. To test hypothesis that the flavor of formula fed to infants modifies their acceptance of some foods, we conducted a within- and between-subjects design study in which two groups of 6- to 11-month-old infants were tested on two separate days. One group was currently feeding a milk-based formula whereas the other was feeding a protein hydrolysate formula, a particularly unpleasant tasting formula to adults that contains similar flavor notes (e.g., sulfur volatiles) with Brassica vegetables such as broccoli. In counterbalanced order, acceptance of pureed broccoli/cauliflower was determined during one test session and pureed carrots on the other. Although there were no group differences in the amount of carrots consumed, hydrolysate infants consumed significantly less broccoli/cauliflower relative to carrots when compared to those who were currently fed milk based formulas (F(1,72 df)=4.43; p=0.04). The mothers of hydrolysate infants were significantly more likely to report that their infants did not enjoy feeding the broccoli/cauliflower (54.2%) when compared to mothers of infants being fed milk-based formulas (28.0%; Chi-Square (1 df)=4.79; p=0.03). Such findings are consistent with prior research that demonstrated a sensory specific satiety following repeated exposure to a particular flavor in milk. We hypothesize that when infants are experiencing a flavor in milk or formula, in the short term, the preference that develops is specific to the context it is experienced in (e.g., milk). Over the longer term, the preference may generalize to other contexts such as solid foods. Hydrolysate infants were also significantly more likely to be judged by their mothers as being more active (F(1,69 df)=3.95; p=0.05) and hesitant (F(1,69 df)=6.55; p=0.01) when compared to those infants who were feeding milk-based formulas, a finding that further supports the hypothesis that mother-child dynamics surrounding early feeding impacts upon mothers' perception of their children's temperament.
Figures
References
-
- Fox MK, Pac S, Devaney B, Jankowski L. Feeding infants and toddler study: what foods are infants and toddlers eating? J Am Diet Assoc. 2004;104:S22–30. - PubMed
-
- Nicklaus S, Boggio V, Chabanet C, Issanchou S. A prospective study on food variety seeking in childhood, adolescence and early adult life. Appetite. 2005;44:289–97. - PubMed
-
- Skinner JD, Carruth BR, Wendy B, Ziegler PJ. Children’s food preferences: a longitudinal analysis. J Am Diet Assoc. 2002;102:1638–46. - PubMed
-
- Lederman SA, Akabas SR, Moore BJ, Bentley ME, Devaney B, Gillman MW, et al. Summary of the presentations at the conference on preventing childhood obesity, December 8, 2003. Pediatrics. 2004;114:1146–73.
-
- Gerrish CJ, Mennella JA. Flavor variety enhances food acceptance in formula-fed infants. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;73:1080–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous