pH dependence of light-driven proton pumping by an archaerhodopsin from Tibet: comparison with bacteriorhodopsin
- PMID: 16473896
- PMCID: PMC1432102
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.105.076547
pH dependence of light-driven proton pumping by an archaerhodopsin from Tibet: comparison with bacteriorhodopsin
Abstract
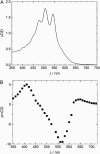
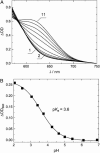
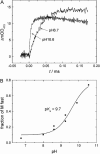
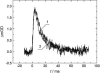
The pH-dependence of photocycle of archaerhodopsin 4 (AR4) was examined, and the underlying proton pumping mechanism investigated. AR4 is a retinal-containing membrane protein isolated from a strain of halobacteria from a Tibetan salt lake. It acts as a light-driven proton pump like bacteriorhodopsin (BR). However, AR4 exhibits an "abnormal" feature--the time sequence of proton release and uptake is reversed at neutral pH. We show here that the temporal sequence of AR4 reversed to "normal"--proton release preceding proton uptake--when the pH is increased above 8.6. We estimated the pK(a) of the proton release complex (PRC) in the M-intermediate to be approximately 8.4, much higher than 5.7 of wide-type BR. The pH-dependence of the rate constant of M-formation shows that the pK(a) of PRC in the initial state of AR4 is approximately 10.4, whereas it is 9.7 in BR. Thus in AR4, the chromophore photoisomerization and subsequent proton transport from the Schiff base to Asp-85 is coupled to a decrease in the pK(a) of PRC from 10.4 to 8.4, which is 2 pK units less than in BR (4 units). This weakened coupling accounts for the lack of early proton release at neutral pH and the reversed time sequence of proton release and uptake in AR4. Nevertheless the PRC in AR4 effectively facilitates deprotonation of primary proton acceptor and recovery of initial state at neutral pH. We found also that all pK(a)s of the key amino acid residues in AR4 were elevated compared to those of BR.
Figures






References
-
- Li, Q. G., Q. G. Sun, W. Zhao, H. Wang, and D. Q. Xu. 2000. Newly isolated archaerhodopsin from a strain of Chinese halobacteria and its proton pumping behavior. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1466:260–266. - PubMed
-
- Wang, H., S. X. Zhan, Q. G. Sun, D. Q. Xu, W. Zhao, W. D. Huang, and Q. G. Li. 2000. Primary structure of helix C to helix G of a new retinal protein in H.sp.xz515. Chin. Sci. Bull. 45:1108–1113.
-
- Wang, Y. R., J. Hong, M. Ming, J. D. Ding, Q. G. Li, and W. D. Huang. 2003. Rapid cloning of an archaerhodopsin gene from Halobacterium species xz515 by LPA. J. Fudan University. 42:577–583.
-
- Mukohata, Y. 1994. Comparative-studies on ion pumps of the bacterial rhodopsin family. Biophys. Chem. 50:191–201. - PubMed
-
- Mukohata, Y., Y. Sugiyama, K. Ihara, and M. Yoshida. 1988. An Australian halobacterium contains a novel proton pump retinal protein: archaerhodopsin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 151:1339–1345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

