The level of reverse transcriptase (RT) in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 particles affects susceptibility to nonnucleoside RT inhibitors but not to lamivudine
- PMID: 16474164
- PMCID: PMC1395365
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.5.2578-2581.2006
The level of reverse transcriptase (RT) in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 particles affects susceptibility to nonnucleoside RT inhibitors but not to lamivudine
Abstract
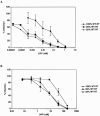
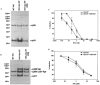
We investigated the relationship between the level of reverse transcriptase (RT) in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) particles and susceptibility to nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs). HIV-1 virions containing different active levels of RT were generated. Susceptibility to the NNRTIs efavirenz and nevirapine was inversely proportional to the level of enzymatically active RT. However, the sensitivity of HIV-1 to the nucleoside analog 3TC was not affected by the level of RT per particle. These data indicate that the susceptibility of HIV-1 to NNRTIs is influenced by RT activity.
Figures


References
-
- Ambrose, Z., V. Boltz, S. Palmer, J. M. Coffin, S. H. Hughes, and V. N. KewalRamani. 2004. In vitro characterization of a simian immunodeficiency virus-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) chimera expressing HIV type 1 reverse transcriptase to study antiviral resistance in pigtail macaques. J. Virol. 78:13553-13561. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arion, D., N. Kaushik, S. McCormick, G. Borkow, and M. A. Parniak. 1998. Phenotypic mechanism of HIV-1 resistance to 3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine (AZT): increased polymerization processivity and enhanced sensitivity to pyrophosphate of the mutant viral reverse transcriptase. Biochemistry 37:15908-15917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

