Downregulation of propranolol-sensitive beta-adrenoceptor signaling after inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis
- PMID: 16474417
- PMCID: PMC1751502
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706675
Downregulation of propranolol-sensitive beta-adrenoceptor signaling after inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis
Erratum in
- Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Aug;148(8):1174
Abstract
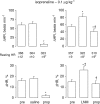
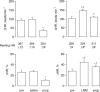
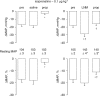
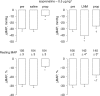
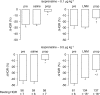
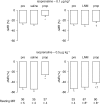
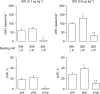
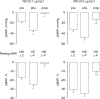
The beta-adrenoceptor agonist, isoprenaline, elicits vasodilation and tachycardia in anesthetized rats via activation of propranolol-sensitive beta1- and beta2-adrenoceptors and also by propranolol-insensitive beta1- and beta3-adrenoceptors. The aim of this study was to determine whether the relative contribution of propranolol-sensitive and -insensitive beta-adrenoceptors to the changes in heart rate (HR) and vascular resistances elicited by isoprenaline is altered after blockade of nitric oxide (NO) synthase, in pentobarbital-anesthetized rats. The hemodynamic responses elicited by isoprenaline (0.1 and 0.5 microg kg(-1), i.v.) were determined before and after injection of saline or the NO synthase inhibitor, N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methylester (L-NAME, 50 micromol kg(-1), i.v.), and again after injection of the beta1- and beta2-adrenoceptor antagonist, propranolol (1 mg kg(-1), i.v.). The responses elicited by the above doses of isoprenaline were also determined before and during infusion of the alpha1-adrenoceptor agonist, phenylephrine (3 microg kg(-1) min(-1), i.v.), and again 15-20 min after injection of propranolol (1.0 mg kg(-1), i.v.). Both doses of isoprenaline elicited tachycardia and reductions in vascular resistances. Propranolol eliminated the responses elicited by the lower dose of isoprenaline and substantially diminished the responses elicited by the higher dose of the beta1-, beta2- and beta3-adrenoceptor agonist. The maximal vasodilator responses elicited by both doses of isoprenaline were not diminished whereas the maximal increases in HR were higher after injection of L-NAME. The ability of propranolol to diminish the hemodynamic actions of isoprenaline was substantially diminished in L-NAME-treated rats, whereas propranolol retained its potency in rats that received an equi-pressor infusion of the alpha1-adrenoceptor agonist, phenylephrine. The finding that the maximal vasodilator responses elicited by isoprenaline were not diminished by L-NAME suggests that the vasodilation elicited by this drug was due to direct activation of beta-adrenoceptors on vascular smooth muscle and that the full compliment of isoprenaline-sensitive receptors was not changed after inhibition of NO synthesis. However, these results suggest that the activities of propranolol-sensitive beta-adrenoceptors are downregulated, whereas propranolol-insensitive beta-adrenoceptors are upregulated upon the loss of exposure to endothelial nitrosyl factors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide (NO) primarily accounts for endothelium-dependent component of beta-adrenoceptor-activated smooth muscle relaxation of mouse aorta in response to isoprenaline.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2002 Oct;38(4-5):87-99. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.38.87. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2002. PMID: 12596888
-
Role of beta2-adrenoceptors (beta-AR), but not beta1-, beta3-AR and endothelial nitric oxide, in beta-AR-mediated relaxation of rat intrapulmonary artery.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2005 Jul;372(1):14-23. doi: 10.1007/s00210-005-1082-2. Epub 2005 Aug 26. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16133491
-
Beta-adrenoceptor dysfunction after inhibition of NO synthesis.Hypertension. 2000 Sep;36(3):376-82. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.36.3.376. Hypertension. 2000. PMID: 10988268
-
A review of the animal pharmacology of labetalol, a combined alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor-blocking drug.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;3(4 Suppl 3):681-4. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976. PMID: 10948 Review.
-
Clinical pharmacology of pindolol.Am Heart J. 1982 Aug;104(2 Pt 2):346-56. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(82)90125-9. Am Heart J. 1982. PMID: 6125094 Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary structured lipids and phytosteryl esters: blood lipids and cardiovascular status in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Lipids. 2008 Jan;43(1):55-64. doi: 10.1007/s11745-007-3124-7. Epub 2007 Nov 6. Lipids. 2008. PMID: 17985171
-
Nitrosyl factors play a vital role in the ventilatory depressant effects of fentanyl in unanesthetized rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Feb;146:112571. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112571. Epub 2021 Dec 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 34953397 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia therapy in calsequestrin-mutant mice.Heart Rhythm. 2010 Nov;7(11):1676-82. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.07.004. Epub 2010 Jul 8. Heart Rhythm. 2010. PMID: 20620233 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
S-Nitroso-L-Cysteine Stereoselectively Blunts the Deleterious Effects of Fentanyl on Breathing While Augmenting Antinociception in Freely-Moving Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 26;13:892307. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.892307. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35721204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BATENBURG W.W., DE VRIES R., SAXENA P.R., DANSER A.H. L-S-nitrosothiols: endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors in porcine coronary arteries. J. Hypertens. 2004a;22:1927–1936. - PubMed
-
- BUNDKIRCHEN A., BRIXIUS K., BOLCK B., SCHWINGER R.H. Bucindolol exerts agonistic activity on the propranolol-insensitive state of β1-adrenoceptors in human myocardium. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002;300:794–801. - PubMed
-
- CLAING A., LAPORTE S.A., CARON M.G., LEFKOWITZ R.J. Endocytosis of G protein-coupled receptors: roles of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and beta-arrestin proteins. Prog. Neurobiol. 2002;66:61–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

