Cytotoxic herpes simplex type 2-specific, DQ0602-restricted CD4 T+-cell clones show alloreactivity to DQ0601
- PMID: 16476054
- PMCID: PMC1782233
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02308.x
Cytotoxic herpes simplex type 2-specific, DQ0602-restricted CD4 T+-cell clones show alloreactivity to DQ0601
Abstract
Alloreactivity is one of the most serious problems in organ transplantation. It has been hypothesized that pre-existing alloreactive T cells are actually cross-reacting cells that have been primed by the autologous major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and a specific peptide. CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes that are alloreactive and recognize a virus-peptide that is presented by the autologous MHC have been reported. Here we demonstrate a cross-reactivity that exists between DQ0602 restricted, herpes simplex type 2 VP16 40-50 specific CD4+ T-cell clones, which can be alloreactive to DQ0601. Though most of the DQ0602 restricted T-cell clones we isolated from two different donors were not alloreactive, weakly cross-reacting T-cell clones could be isolated from both donors. Two strongly cross-reacting T-cell clones with high affinity interaction of their T-cell receptor (TCR) with both DQ0602/VP16 40-50 and DQ0601 could be isolated from one donor. DNA sequencing of the a fragment of the Vbeta gene used in their TCR confirmed that these two T cells indeed are two independent clones. These clones are cytotoxic and produce cytokines of a T helper 2-like pattern. Possible implications in a DR-matched transplantation setting are discussed.
Figures
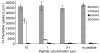


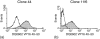
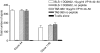

Similar articles
-
Distinct T cell interactions with HLA class II tetramers characterize a spectrum of TCR affinities in the human antigen-specific T cell response.J Immunol. 2000 Dec 15;165(12):6994-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.12.6994. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11120826
-
Human TCR-gamma/delta alloreactive response to HLA-DR molecules. Comparison with response of TCR-alpha/beta.J Immunol. 1994 Oct 1;153(7):2890-904. J Immunol. 1994. PMID: 8089476
-
Mutational analysis of critical residues determining antigen presentation and activation of HLA-DQ0602 restricted T-cell clones.Hum Immunol. 2002 Mar;63(3):185-93. doi: 10.1016/s0198-8859(01)00377-9. Hum Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11872236
-
HLA-DQ tetramers identify epitope-specific T cells in peripheral blood of herpes simplex virus type 2-infected individuals: direct detection of immunodominant antigen-responsive cells.J Immunol. 2000 Apr 15;164(8):4244-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.8.4244. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10754321
-
Cross-Reactivity of TCR Repertoire: Current Concepts, Challenges, and Implication for Allotransplantation.Front Immunol. 2016 Mar 24;7:89. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00089. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27047489 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Donor-derived CD4(+)/CCR7(+) T-cell partial selective depletion does not alter acquired anti-infective immunity.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014 May;49(5):611-5. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2014.6. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014. PMID: 24566708
-
Alloreactivity across HLA barriers is mediated by both naïve and antigen-experienced T cells.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011 Jun;17(6):800-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.12.711. Epub 2011 Jan 6. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21215812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Opelz G, Wujciak T, Dohler B, Scherer S, Mytilineos J. HLA compatibility and organ transplant survival. Collaborative Transplant Study Rev Immunogenet. 1999;1:334–42. - PubMed
-
- Sayegh MH, Watschinger B, Carpenter CB. Mechanisms of T cell recognition of alloantigen. The role of peptides. Transplantation. 1994;57:1295–302. - PubMed
-
- Pawelec G, Adibzadeh M, Bornhak S, et al. The role of endogenous peptides in the direct pathway of alloreactivity to human MHC class II molecules expressed on CHO cells. Immunol Rev. 1996;154:155–73. - PubMed
-
- Steinle A, Reinhardt C, Jantzer P, Schendel DJ. In vivo expansion of HLA-B35 alloreactive T cells sharing homologous T cell receptors: evidence for maintenance of an oligoclonally dominated allospecificity by persistent stimulation with an autologous MHC/peptide complex. J Exp Med. 1995;181:503–13. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

