Human antibodies induce arthritis in mice deficient in the low-affinity inhibitory IgG receptor Fc gamma RIIB
- PMID: 16476768
- PMCID: PMC2118221
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20051951
Human antibodies induce arthritis in mice deficient in the low-affinity inhibitory IgG receptor Fc gamma RIIB
Abstract
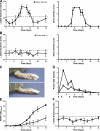
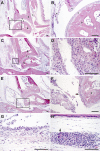
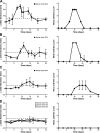
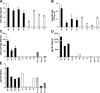
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex autoimmune disease with a poorly understood pathogenesis. The disease is associated with polyclonal B cell activation and the production of autoantibodies (autoAbs), but there is a longstanding controversy as to whether such Abs contribute to, or are secondary to, the pathogenesis of RA. To address the potential pathogenicity of human RA-associated Abs, we developed a passive transfer model involving mice deficient in the low-affinity inhibitory Fc receptor, FcgammaRIIB. We report that plasma or serum from patients with active RA can induce inflammation and histological lesions in FcgammaRIIB-/- mice consistent with arthritis, and that this pathogenic activity is caused by the immunoglobulin G-rich fraction. Our results suggest that humoral autoimmunity can contribute directly to autoimmune arthritis, and that FcgammaRIIB-/- mice are a promising model to evaluate the arthritogenic potential of human autoAbs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Essential role of Fc gamma receptors in anti-type II collagen antibody-induced arthritis.J Immunol. 2003 Apr 15;170(8):4318-24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.8.4318. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12682268
-
Sialylated Autoantigen-Reactive IgG Antibodies Attenuate Disease Development in Autoimmune Mouse Models of Lupus Nephritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 6;9:1183. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01183. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29928274 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting Edge: The murine high-affinity IgG receptor FcγRIV is sufficient for autoantibody-induced arthritis.J Immunol. 2011 Feb 15;186(4):1899-903. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003642. Epub 2011 Jan 19. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21248252
-
A role of FcgammaRIIB in the development of collagen-induced arthritis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2004 Jun;58(5):292-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2004.04.005. Biomed Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15194165 Review.
-
Pathogenic antibody recognition of cartilage.Cell Tissue Res. 2010 Jan;339(1):213-20. doi: 10.1007/s00441-009-0816-8. Epub 2009 Jun 9. Cell Tissue Res. 2010. PMID: 19506910 Review.
Cited by
-
The structure, specificity and function of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019 Aug;15(8):503-508. doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0244-4. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31253945 Review.
-
Clinical approaches to early inflammatory arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009 Nov;5(11):627-33. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.203. Epub 2009 Sep 29. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19786990 Review.
-
Could the expression of CD86 and FcγRIIB on B cells be functionally related and involved in driving rheumatoid arthritis?Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(4):133. doi: 10.1186/ar3092. Epub 2010 Aug 13. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20735866 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically engineered humanized mouse models for preclinical antibody studies.BioDrugs. 2014 Apr;28(2):171-80. doi: 10.1007/s40259-013-0071-0. BioDrugs. 2014. PMID: 24150980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting IgG in Arthritis: Disease Pathways and Therapeutic Avenues.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 28;19(3):677. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030677. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29495570 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Feldmann, M., F.M. Brennan, and R.N. Maini. 1996. Rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. 85:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Dorner, T., K. Egerer, E. Feist, and G.R. Burmester. 2004. Rheumatoid factor revisited. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 16:246–253. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto, I., D.M. Lee, R. Goldbach-Mansky, T. Sumida, C.A. Hitchon, P.H. Schur, R.J. Anderson, J.S. Coblyn, M.E. Weinblatt, M. Brenner, et al. 2003. Low prevalence of antibodies to glucose-6-phosphate isomerase in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and a spectrum of other chronic autoimmune disorders. Arthritis Rheum. 48:944–954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

