trt-1 is the Caenorhabditis elegans catalytic subunit of telomerase
- PMID: 16477310
- PMCID: PMC1361356
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020018
trt-1 is the Caenorhabditis elegans catalytic subunit of telomerase
Abstract
Mutants of trt-1, the Caenorhabditis elegans telomerase reverse transcriptase, reproduce normally for several generations but eventually become sterile as a consequence of telomere erosion and end-to-end chromosome fusions. Telomere erosion and uncapping do not cause an increase in apoptosis in the germlines of trt-1 mutants. Instead, late-generation trt-1 mutants display chromosome segregation defects that are likely to be the direct cause of sterility. trt-1 functions in the same telomere replication pathway as mrt-2, a component of the Rad9/Rad1/Hus1 (9-1-1) proliferating cell nuclear antigen-like sliding clamp. Thus, the 9-1-1 complex may be required for telomerase to act at chromosome ends in C. elegans. Although telomere erosion limits replicative life span in human somatic cells, neither trt-1 nor telomere shortening affects postmitotic aging in C. elegans. These findings illustrate effects of telomere dysfunction in C. elegans mutants lacking the catalytic subunit of telomerase, trt-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
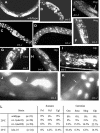
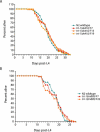
Similar articles
-
High incidence of rapid telomere loss in telomerase-deficient Caenorhabditis elegans.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 10;34(1):96-103. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj417. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16407328 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans POT-1 and POT-2 repress telomere maintenance pathways.G3 (Bethesda). 2013 Feb;3(2):305-13. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.004440. Epub 2013 Feb 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 23390606 Free PMC article.
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans Rad17 homolog HPR-17 is required for telomere replication.Genetics. 2007 May;176(1):703-9. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.070201. Epub 2007 Mar 4. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17339221 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue formation and tissue engineering through host cell recruitment or a potential injectable cell-based biocomposite with replicative potential: Molecular mechanisms controlling cellular senescence and the involvement of controlled transient telomerase activation therapies.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015 Dec;103(12):3993-4023. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.35515. Epub 2015 Aug 14. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015. PMID: 26034007 Review.
-
Cellular functions of the dual-targeted catalytic subunit of telomerase, telomerase reverse transcriptase--potential role in senescence and aging.Exp Gerontol. 2014 Aug;56:189-93. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2014.02.011. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Exp Gerontol. 2014. PMID: 24583100 Review.
Cited by
-
TERRA expression is regulated by the telomere-binding proteins POT-1 and POT-2 in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Oct 27;51(19):10681-10699. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad742. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37713629 Free PMC article.
-
Human telomerase model shows the role of the TEN domain in advancing the double helix for the next polymerization step.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jun 7;108(23):9443-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015399108. Epub 2011 May 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21606328 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans whole-genome sequencing reveals mutational signatures related to carcinogens and DNA repair deficiency.Genome Res. 2014 Oct;24(10):1624-36. doi: 10.1101/gr.175547.114. Epub 2014 Jul 16. Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 25030888 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans RSD-2 and RSD-6 promote germ cell immortality by maintaining small interfering RNA populations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Oct 14;111(41):E4323-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406131111. Epub 2014 Sep 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25258416 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans POT-2 telomere protein represses a mode of alternative lengthening of telomeres with normal telomere lengths.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 May 15;109(20):7805-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1119191109. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22547822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakamura TM, Morin GB, Chapman KB, Weinrich SL, Andrews WH, et al. Telomerase catalytic subunit homologs from fission yeast and human. Science. 1997;277:955–959. - PubMed
-
- Meyerson M, Counter CM, Eaton EN, Ellisen LW, Steiner P, et al. hEST2, the putative human telomerase catalytic subunit gene, is up-regulated in tumor cells and during immortalization. Cell. 1997;90:785–795. - PubMed
-
- Greider CW, Blackburn EH. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature. 1989;337:331–337. - PubMed
-
- Lingner J, Cooper JP, Cech TR. Telomerase and DNA end replication: No longer a lagging strand problem? Science. 1995;269:1533–1534. - PubMed
-
- Harley CB, Futcher AB, Greider CW. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1990;345:458–460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

