GCUNC-45 is a novel regulator for the progesterone receptor/hsp90 chaperoning pathway
- PMID: 16478993
- PMCID: PMC1430258
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.26.5.1722-1730.2006
GCUNC-45 is a novel regulator for the progesterone receptor/hsp90 chaperoning pathway
Abstract
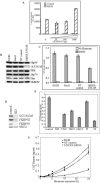
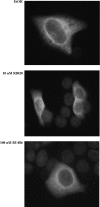
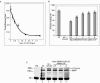
The hsp90 chaperoning pathway is a multiprotein system that is required for the production or activation of many cell regulatory proteins, including the progesterone receptor (PR). We report here the identity of GCUNC-45 as a novel modulator of PR chaperoning by hsp90. GCUNC-45, previously implicated in the activities of myosins, can interact in vivo and in vitro with both PR-A and PR-B and with hsp90. Overexpression and knockdown experiments show GCUNC-45 to be a positive factor in promoting PR function in the cell. GCUNC-45 binds to the ATP-binding domain of hsp90 to prevent the activation of its ATPase activity by the cochaperone Aha1. This effect limits PR chaperoning by hsp90, but this can be reversed by FKBP52, a cochaperone that is thought to act later in the pathway. These findings reveal a new cochaperone binding site near the N terminus of hsp90, add insight on the role of FKBP52, and identify GCUNC-45 as a novel regulator of the PR signaling pathway.
Figures





References
-
- Barral, J. M., A. H. Hutagalung, A. Brinker, F. U. Hartl, and H. F. Epstein. 2002. Role of the myosin assembly protein UNC-45 as a molecular chaperone for myosin. Science 295:669-671. - PubMed
-
- Blatch, G. L., and M. Lassle. 1999. The tetratricopeptide repeat: a structural motif mediating protein-protein interactions. BioEssays 21:932-939. - PubMed
-
- Brinker, A., C. Scheufler, F. von der Mülbe, B. Fleckenstein, C. Herrmann, G. Jung, I. Moarefi, and F. U. Hartl. 2002. Ligand discrimination by TPR domains. J. Biol. Chem. 277:19265-19275. - PubMed
-
- Carrello, A., E. Ingley, R. F. Minchin, S. Tsai, and T. Ratajczak. 1999. The common tetratricopeptide repeat acceptor site for steroid receptor-associated immunophilins and Hop is located in the dimerization domain of hsp90. J. Biol. Chem. 274:2682-2689. - PubMed
-
- Carrigan, P. E., G. M. Nelson, P. J. Roberts, J. N. Stoffer, D. L. Riggs, and D. F. Smith. 2004. Multiple domains of the co-chaperone Hop are important for Hsp70 binding. J. Biol. Chem. 279:16185-16193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
