Assessment of fluid shifts of body compartments using both bioimpedance analysis and blood volume monitoring
- PMID: 16479069
- PMCID: PMC2733983
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.1.75
Assessment of fluid shifts of body compartments using both bioimpedance analysis and blood volume monitoring
Abstract
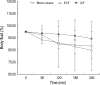
Fluid shifts are commonplace in chronic hemodialysis patients during the intra- and interdialytic periods. In this study, we evaluated fluid shifts of body compartments using both bioimpedance spectroscopy and blood volume monitoring from the start to the end of hemodialysis. 24 stable hemodialysis patients were included on the study. Relative change of blood volume was progressively reduced from the start to the end of hemodialysis (1 hr, -7.22+/-3.23%; 2 hr, -9.78+/-4.69%; 3 hr, -12.88+/-5.65%; 4 hr, -15.41+/-6.54%, respectively). Mean % reduction of intracellular fluid was not significantly different to that of extracellular fluid at the end of hemodialysis (delta ICF, -6.58+/-5.34% vs. delta ECF, -7.07+/-5.12%). Mean % fluid reduction of arms, legs and trunk was -11.98+/-6.76%, -6.43+/-4.37% and -7.47+/-4.56%, respectively at the end of hemodialysis. There were 3 characteristic patterns in blood-volume change. Similar amounts of fluid were removed from the extracellular and intracellular compartments during hemodialysis, with the arms showing the greatest loss in terms of body segments. The pattern of blood volume change measured by blood volume monitoring may be useful for more accurate determination of dry-weight and for correcting volume status in hemodialysis patients.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preserving central blood volume: changes in body fluid compartments during hemodialysis.ASAIO J. 2001 Nov-Dec;47(6):615-8. doi: 10.1097/00002480-200111000-00009. ASAIO J. 2001. PMID: 11730198
-
Bioimpedance resistance ratios for the evaluation of dry weight in hemodialysis.Clin Nephrol. 2000 Feb;53(2):108-14. Clin Nephrol. 2000. PMID: 10711412
-
[Measurement of fluid compartments using electrical bioimpedance for assessment of target weight in hemodialysis patients].Przegl Lek. 2000;57(12):707-10. Przegl Lek. 2000. PMID: 11398591 Clinical Trial. Polish.
-
Do changes in relative blood volume monitoring correlate to hemodialysis-associated hypotension?Nephron Clin Pract. 2011;117(3):c179-83. doi: 10.1159/000320196. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011. PMID: 20805690 Review.
-
Assessment of extracellular fluid volume and fluid status in hemodialysis patients: current status and technical advances.Semin Dial. 2012 Jul;25(4):377-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-139X.2012.01095.x. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Semin Dial. 2012. PMID: 22686593 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimized Blood Volume Monitoring during Hemodialysis Procedure based on Ultrasonic Speed Measurement.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2019 Jun 1;9(3):373-380. doi: 10.31661/jbpe.v9i3Jun.675. eCollection 2019 Jun. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2019. PMID: 31341883 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the content of intracellular and extracellular fluid and the amount of water intake among Chinese college students.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2019 Sep 18;16:67. doi: 10.1186/s12986-019-0397-9. eCollection 2019. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31548843 Free PMC article.
-
Inferior vena cava/aorta diameter index in the assessment of the body fluid status - a comparative study of measurements performed by experienced and inexperienced examiners in a group of young adults.J Ultrason. 2014 Sep;14(58):273-9. doi: 10.15557/JoU.2014.0027. Epub 2014 Sep 30. J Ultrason. 2014. PMID: 26675322 Free PMC article.
-
The Feasibility of Semi-Continuous and Multi-Frequency Thoracic Bioimpedance Measurements by a Wearable Device during Fluid Changes in Hemodialysis Patients.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 15;24(6):1890. doi: 10.3390/s24061890. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38544153 Free PMC article.
-
The time of onset of intradialytic hypotension during a hemodialysis session associates with clinical parameters and mortality.Kidney Int. 2021 Jun;99(6):1408-1417. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.01.018. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Kidney Int. 2021. PMID: 33607178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henderson LW. Symptomatic hypotension during hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 1980;17:571–576. - PubMed
-
- Jack QJ, Ravindra LM. Assessment of dry weight in hemodialysis: An overview. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:392–403. - PubMed
-
- Ishibe S, Peixoto AJ. Methods of assessment of volume status and intercompartmental fluid shifts in hemodialysis patients: implications in clinical practice. Semin Dial. 2004;17:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Kouw PM, Kooman JP, Cheriex EC, Olthof CG, de Vries PM, Leunissen KM. Assessment of postdialysis dry weight: a comparison of techniques. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1993;4:98–104. - PubMed
-
- Lauster F, Gerzer R, Weil J, Fulle HJ, Schiffl H. Assessment of dry body weight in hemodialysis patients by the biochemical marker cGMP. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1990;5:356–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

