Efficacy of low level laser therapy on neurosensory recovery after injury to the inferior alveolar nerve
- PMID: 16480503
- PMCID: PMC1386654
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-160X-2-3
Efficacy of low level laser therapy on neurosensory recovery after injury to the inferior alveolar nerve
Abstract
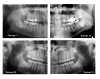
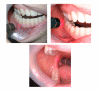
Background: The most severe complication after the removal of mandibular third molars is injury to the inferior alveolar nerve or the lingual nerve. These complications are rather uncommon (0.4% to 8.4%) and most of them are transient. However, some of them persist for longer than 6 months, which can leave various degrees of long-term permanent disability. While several methods such as pharmacologic therapy, microneurosurgery, autogenous and alloplastic grafting can be used for the treatment of long-standing sensory aberrations in the inferior alveolar nerve, there are few reports regarding low level laser treatment. This paper reports the effects of low level laser therapy in 4 patients with longstanding sensory nerve impairment following mandibular third molar surgery.
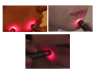
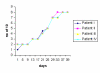
Methods: Four female patients had complaints of paresthesia and dysesthesia of the lip, chin and gingiva, and buccal regions. Each patient had undergone mandibular third molar surgery at least 1 year before. All patients were treated with low level laser therapy. Clinical neurosensory tests (the brush stroke directional discrimination test, 2-point discrimination test, and a subjective assessment of neurosensory function using a visual analog scale) were used before and after treatment, and the responses were plotted over time.
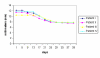
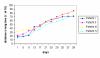
Results: When the neurosensory assessment scores after treatment with LLL therapy were compared with the baseline values prior to treatment, there was a significant acceleration in the time course, as well as in the magnitude, of neurosensory return. The VAS analysis revealed progressive improvement over time.
Conclusion: Low level laser therapy seemed to be conducive to the reduction of long-standing sensory nerve impairment following third molar surgery. Further studies are worthwhile regarding the clinical application of this treatment modality.
Figures
References
-
- Benediktsdottir IS, Wenzel A, Petersen JK, Hintze H. Mandibular third molar removal: risk indicators for extended operation time, postoperative pain, and complications. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004;97:438–446. - PubMed
-
- Smith AC, Barry SE, Chiong AY, Hadzakis D, Kha SL, Mok SC, Sable DL. Inferior alveolar nerve damage following removal of mandibular third molar teeth. A prospective study using panoramic radiography. Aust Dent J. 1997;42:149–152. - PubMed
-
- Miloro M, Halkias LE, Mallery S, Travers S, Rashid RG. Low-level laser effect on neural regeneration in Gore-Tex tubes. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;93:27–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

