Death from colonic disease in epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica
- PMID: 16480504
- PMCID: PMC1431558
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-5945-6-2
Death from colonic disease in epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica
Abstract
Background: Squamous cell carcinomas and renal failure were reported the causes of death in patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB). Death from colonic disease in epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is never reported.
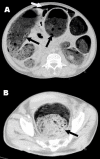
Case presentation: We demonstrate a male patient with RDEB. He suffered megacolon due to fecal impaction and died from sigmoid colon perforation with peritonitis at age 35 years.
Conclusion: Constipation is a common clinical feature of RDEB, but fetal complications of chronic constipation are rarely reported. To the author's best knowledge, it has not been reported or recognized in the English literature previously. The aggressive assessment of constipation with fecal impaction is recommended in patients with RDEB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inherited epidermolysis bullosa and the risk of death from renal disease: experience of the National Epidermolysis Bullosa Registry.Am J Kidney Dis. 2004 Oct;44(4):651-60. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004. PMID: 15384016
-
Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa associated with mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis and multifocal necrotizing leucoencephalopathy of the pons.Br J Dermatol. 2004 Dec;151(6):1266-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06267.x. Br J Dermatol. 2004. PMID: 15606525
-
Squamous cell carcinoma complicating recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa-Hallopeau-Siemens: a report of four cases.Int J Dermatol. 2009 Jun;48(6):588-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04006.x. Int J Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 19538366
-
Management of squamous cell carcinoma in a patient with recessive-type epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica.Dermatol Surg. 2004 Nov;30(11):1424-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.2004.30440.x. Dermatol Surg. 2004. PMID: 15522026 Review.
-
Effective esophageal balloon dilation for esophageal stenosis in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa.Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2006 Apr;16(2):115-9. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-923991. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2006. PMID: 16685618 Review.
Cited by
-
Severe Generalized Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex in Two Hong Kong Children due to De Novo Variants in KRT14 and KRT5.Case Rep Pediatr. 2020 Apr 17;2020:4206348. doi: 10.1155/2020/4206348. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32351751 Free PMC article.
-
First successful preimplantation genetic diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia: case study of a novel c.4505-4508insACTC mutation.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2012 Apr;29(4):347-52. doi: 10.1007/s10815-012-9728-8. Epub 2012 Feb 22. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2012. PMID: 22354727 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pain care for patients with epidermolysis bullosa: best care practice guidelines.BMC Med. 2014 Oct 9;12:178. doi: 10.1186/s12916-014-0178-2. BMC Med. 2014. PMID: 25603875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kero M. Occurrence of epidermolysis bullosa in Finland. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh) 1984;64:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Pavicic Z, Kmet-Vizintin P, Kansky A, Dobric I. Occurrence of hereditary epidermolysis bullosa in Croatia. Pediatr Dermatol. 1990;7:108–10. - PubMed
-
- McKenna KE, Walsh MY, Bingham EA. Epidermolysis bullosa in Northern Ireland. Br J Dermatol. 1992;127:318–21. - PubMed
-
- Abahussein AA, Al-zayir AA, Mostafa WZ, Okoro AN. Epidermolysis bullosa in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:579–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources