The thrombopoietin receptor, c-Mpl, is a selective surface marker for human hematopoietic stem cells
- PMID: 16480521
- PMCID: PMC1402332
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-4-9
The thrombopoietin receptor, c-Mpl, is a selective surface marker for human hematopoietic stem cells
Abstract
Background: Thrombopoietin (TPO), the primary cytokine regulating megakaryocyte proliferation and differentiation, exerts significant influence on other hematopoietic lineages as well, including erythroid, granulocytic and lymphoid lineages. We previously demonstrated that the receptor for TPO, c-mpl, is expressed by a subset of human adult bone marrow hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSC/PC) that are enriched for long-term multilineage repopulating ability in the SCID-hu Bone in vivo model of human hematopoiesis.
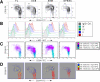
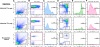
Methods: Here, we employ flow cytometry and an anti-c-mpl monoclonal antibody to comprehensively define the surface expression pattern of c-mpl in four differentiation stages of human CD34+ HSC/PC (I: CD34+38--, II: CD34+38dim, III: CD34+38+, IV: CD34dim38+) for the major sources of human HSC: fetal liver (FL), umbilical cord blood (UCB), adult bone marrow (ABM), and cytokine-mobilized peripheral blood stem cells (mPBSC). We use a surrogate in vivo model of human thymopoiesis, SCID-hu Thy/Liv, to compare the capacity of c-mpl+ vs. c-mpl-- CD34+38--/dim HSC/PC for thymocyte reconstitution.
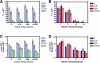
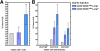
Results: For all tissue sources, the percentage of c-mpl+ cells was significantly highest in stage I HSC/PC (FL 72 +/- 10%, UCB 67 +/- 19%, ABM 82 +/- 16%, mPBSC 71 +/- 15%), and decreased significantly through stages II, III, and IV ((FL 3 +/- 3%, UCB 8 +/- 13%, ABM 0.6 +/- 0.6%, mPBSC 0.2 +/- 0.1%) [ANOVA: P < 0.0001]. The relative median fluorescence intensity of c-mpl expression was similarly highest in stage I, decreasing through stage IV [ANOVA: P < 0.0001]. No significant differences between tissue sources were observed for either % c-mpl+ cells [P = 0.89] or intensity of c-mpl expression [P = 0.21]. Primary Thy/Liv grafts injected with CD34+38--/dimc-mpl+ cells showed slightly higher levels of donor HLA+ thymocyte reconstitution vs. CD34+38--/dimc-mpl---injected grafts and non-injected controls (c-mpl+ vs. c-mpl--: CD2+ 6.8 +/- 4.5% vs. 2.8 +/- 3.3%, CD4+8-- 54 +/- 35% vs. 31 +/- 29%, CD4--8+ 29 +/- 19% vs. 18 +/- 14%).
Conclusion: These findings support the hypothesis that the TPO receptor, c-mpl, participates in the regulation of primitive human HSC from mid-fetal through adult life. This study extends our previous work documenting human B-lineage, myeloid and CD34+ cell repopulation by c-mpl+ progenitors to show that c-mpl+ HSC/PC are also capable of significant T-lineage reconstitution in vivo. These results suggest that c-mpl merits consideration as a selective surface marker for the identification and isolation of human HSC in both basic research and clinical settings.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD34+ cells from mobilized peripheral blood retain fetal bone marrow repopulating capacity within the Thy-1+ subset following cell division ex vivo.Exp Hematol. 1999 Jun;27(6):994-1003. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(99)00030-2. Exp Hematol. 1999. PMID: 10378888
-
Targeting c-Mpl for revival of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-induced hematopoietic inhibition when CD34+ progenitor cells are re-engrafted into a fresh stromal microenvironment in vivo.J Virol. 2004 Oct;78(20):11385-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.20.11385-11392.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15452260 Free PMC article.
-
Human allogeneic stem cell maintenance and differentiation in a long-term multilineage SCID-hu graft.Blood. 1995 Sep 1;86(5):1680-93. Blood. 1995. PMID: 7655000
-
Thrombopoietin: expression of its receptor MPL and proliferative effects on leukemic cells.Leukemia. 1996 Sep;10(9):1405-21. Leukemia. 1996. PMID: 8751457 Review.
-
Hierarchical structure of human megakaryocyte progenitor cells.Stem Cells. 1996;14 Suppl 1:75-81. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530140709. Stem Cells. 1996. PMID: 11012205 Review.
Cited by
-
Activating SRC/MAPK signaling via 5-HT1A receptor contributes to the effect of vilazodone on improving thrombocytopenia.Elife. 2024 Apr 4;13:RP94765. doi: 10.7554/eLife.94765. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38573820 Free PMC article.
-
On the Quest for In Vitro Platelet Production by Re-Tailoring the Concepts of Megakaryocyte Differentiation.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Dec 3;56(12):671. doi: 10.3390/medicina56120671. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 33287459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematopoietic stem cells and extramedullary hematopoiesis in the lungs.Cytometry A. 2023 Dec;103(12):967-977. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.24804. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Cytometry A. 2023. PMID: 37807901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelets at the Vessel Wall in Non-Thrombotic Disease.Circ Res. 2023 Mar 17;132(6):775-790. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321566. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Circ Res. 2023. PMID: 36927182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incomplete restoration of Mpl expression in the mpl-/- mouse produces partial correction of the stem cell-repopulating defect and paradoxical thrombocytosis.Blood. 2009 Feb 19;113(8):1778-85. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-11-124859. Epub 2008 Sep 16. Blood. 2009. PMID: 18796624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yin AH, Miraglia S, Zanjani ED, Almeida-Porada G, Ogawa M, Leary AG, Olweus J, Kearney J, Buck DW. AC133, a novel marker for human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Blood. 1997;90:5002–5012. - PubMed
-
- Civin CI, Strauss LC, Brovall C, Fackler MJ, Schwartz JF, Shaper JH. Antigenic analysis of hematopoiesis. III. A hematopoietic progenitor cell surface antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody raised against KG-1a cells. J Immunol. 1984;133:157–165. - PubMed
-
- Krause DS, Fackler MJ, Civin CI, May WS. CD34: structure, biology, and clinical utility. Blood. 1996;87:1–13. - PubMed
-
- DiGiusto D, Chen S, Combs J, Webb S, Namikawa R, Tsukamoto A, Chen BP, Galy AH. Human fetal bone marrow early progenitors for T, B, and myeloid cells are found exclusively in the population expressing high levels of CD34. Blood. 1994;84:421–432. - PubMed
-
- Civin CI, Almeida-Porada G, Lee MJ, Olweus J, Terstappen LW, Zanjani ED. Sustained, retransplantable, multilineage engraftment of highly purified adult human bone marrow stem cells in vivo. Blood. 1996;88:4102–4109. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

