The Ras-GRF1 exchange factor coordinates activation of H-Ras and Rac1 to control neuronal morphology
- PMID: 16481401
- PMCID: PMC1446076
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-10-0913
The Ras-GRF1 exchange factor coordinates activation of H-Ras and Rac1 to control neuronal morphology
Abstract
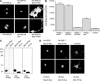
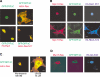
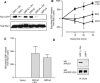
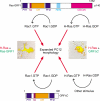
The Ras-GRF1 exchange factor has regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity for H-Ras and Rac1 through separate domains. Both H-Ras and Rac1 activation have been linked to synaptic plasticity and thus could contribute to the function of Ras-GRF1 in neuronal signal transduction pathways that underlie learning and memory. We defined the effects of Ras-GRF1 and truncation mutants that include only one of its GEF activities on the morphology of PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells. Ras-GRF1 required coexpression of H-Ras to induce morphological effects. Ras-GRF1 plus H-Ras induced a novel, expanded morphology in PC12 cells, which was characterized by a 10-fold increase in soma size and by neurite extension. A truncation mutant of Ras-GRF1 that included the Ras GEF domain, GRFdeltaN, plus H-Ras produced neurite extensions, but did not expand the soma. This neurite extension was blocked by inhibition of MAP kinase activation, but was independent of dominant-negative Rac1 or RhoA. A truncation mutant of Ras-GRF1 that included the Rac GEF domains, GRFdeltaC, produced the expanded phenotype in cotransfections with H-Ras. Cell expansion was inhibited by wortmannin or dominant-negative forms of Rac1 or Akt. GRFdeltaC binds H-Ras.GTP in both pulldown assays from bacterial lysates and by coimmunoprecipitation from HEK293 cells. These results suggest that coordinated activation of H-Ras and Rac1 by Ras-GRF1 may be a significant controller of neuronal cell size.
Figures




References
-
- Arendt, T. et al. (2004). Neuronal activation of Ras regulates synaptic connectivity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 19, 2953–2966. - PubMed
-
- Aznar, S., and Lacal, J. C. (2001). Rho signals to cell growth and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 165, 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Baouz, S., Jacquet, E., Bernardi, A., and Parmeggiani, A. (1997). The N-terminal moiety of CDC25(Mm), a GDP/GTP exchange factor of Ras proteins, controls the activity of the catalytic domain. Modulation by calmodulin and calpain. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 6671–6676. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Sagi, D., and Feramisco, J. R. (1985). Microinjection of the Ras oncogene protein into PC12 cells induces morphological differentiation. Cell 42, 841–848. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

