Functional dissection of Reelin signaling by site-directed disruption of Disabled-1 adaptor binding to apolipoprotein E receptor 2: distinct roles in development and synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 16481437
- PMCID: PMC6674917
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4566-05.2006
Functional dissection of Reelin signaling by site-directed disruption of Disabled-1 adaptor binding to apolipoprotein E receptor 2: distinct roles in development and synaptic plasticity
Abstract
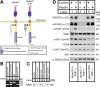
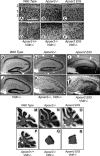
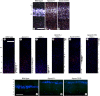
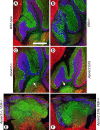
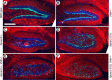
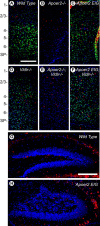
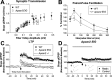
The Reelin signaling pathway controls neuronal positioning in human and mouse brain during development as well as modulation of long-term potentiation (LTP) and behavior in the adult. Reelin signals by binding to two transmembrane receptors, apolipoprotein E receptor 2 (Apoer2) and very-low-density lipoprotein receptor. After Reelin binds to the receptors, Disabled-1 (Dab1), an intracellular adaptor protein that binds to the cytoplasmic tails of the receptors, becomes phosphorylated on tyrosine residues, initiating a signaling cascade that includes activation of Src-family kinases and Akt. Here, we have created a line of mutant mice (Apoer2 EIG) in which the Apoer2 NFDNPVY motif has been altered to EIGNPVY to disrupt the Apoer2-Dab1 interaction to further study Reelin signaling in development and adult brain. Using primary neuronal cultures stimulated with recombinant Reelin, we find that normal Reelin signaling requires the wild-type NFDNPVY sequence and likely the interaction of Apoer2 with Dab1. Furthermore, examination of hippocampal, cortical, and cerebellar layering reveals that the NFDNPVY sequence of Apoer2 is indispensable for normal neuronal positioning during development of the brain. Adult Apoer2 EIG mice display severe abnormalities in LTP and behavior that are distinct from those observed for mice lacking Apoer2. In Apoer2 EIG slices, LTP degraded to baseline within 30 min, and this was prevented in the presence of Reelin. Together, these findings emphasize the complexity of Reelin signaling in the adult brain, which likely requires multiple adaptor protein interactions with the intracellular domain of Apoer2.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen OM, Yeung CH, Vorum H, Wellner M, Andreassen TK, Erdmann B, Mueller EC, Herz J, Otto A, Cooper TG, Willnow TE (2003). Essential role of the apolipoprotein E receptor-2 in sperm development. J Biol Chem 278:23989–23995. - PubMed
-
- Arnaud L, Ballif BA, Forster E, Cooper JA (2003). Fyn tyrosine kinase is a critical regulator of disabled-1 during brain development. Curr Biol 13:9–17. - PubMed
-
- Assadi AH, Zhang G, Beffert U, McNeil RS, Renfro AL, Niu S, Quattrocchi CC, Antalffy BA, Sheldon M, Armstrong DD, Wynshaw-Boris A, Herz J, D’Arcangelo G, Clark GD (2003). Interaction of reelin signaling and Lis1 in brain development. Nat Genet 35:270–276. - PubMed
-
- Beffert U, Morfini G, Bock HH, Reyna H, Brady ST, Herz J (2002). Reelin-mediated signaling locally regulates protein kinase B/Akt and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Biol Chem 277:49958–49964. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
