Acetylation of Stat1 modulates NF-kappaB activity
- PMID: 16481475
- PMCID: PMC1369049
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.364306
Acetylation of Stat1 modulates NF-kappaB activity
Abstract
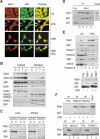
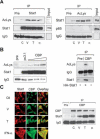
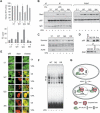
Acetylation of signaling molecules can lead to apoptosis or differentiation of carcinoma cells. The molecular mechanisms underlying these processes and the biological role of enzymes mediating the transfer or removal of an acetyl-group are currently under intense investigation. Our study shows that Stat1 is an acetylated protein. Stat1 acetylation depends on the balance between Stat1-associated histone deacetylases (HDACs) and histone acetyltransferases (HATs) such as CBP. Remarkably both inhibitors of HDACs and the cytokine interferon alpha alter this equilibrium and induce Stat1 acetylation. The analysis of Stat1 mutants reveals Lys 410 and Lys 413 as acetylation sites. Experiments with Stat1 mutants mimicking either constitutively acetylated or nonacetylated states show that only acetylated Stat1 is able to interact with NF-kappaB p65. As a consequence, p65 DNA binding, nuclear localization, and expression of anti-apoptotic NF-kappaB target genes decrease. These findings show how the acetylation of Stat1 regulates NF-kappaB activity and thus ultimately apoptosis.
Figures
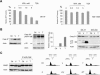
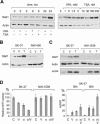
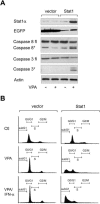
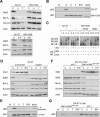

Similar articles
-
Regulation of NF-kappaB action by reversible acetylation.Novartis Found Symp. 2004;259:208-17; discussion 218-25. Novartis Found Symp. 2004. PMID: 15171256 Review.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors block IFNγ-induced STAT1 phosphorylation.Cell Signal. 2012 Jul;24(7):1453-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.02.018. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 22425562
-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, inhibits EBV-induced B lymphocyte transformation via suppression of RelA acetylation.Cancer Res. 2009 Jan 15;69(2):583-92. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2442. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19147572
-
Histone deacetylase inhibition down-regulates cyclin D1 transcription by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB/p65 DNA binding.Mol Cancer Res. 2005 Feb;3(2):100-9. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-04-0070. Mol Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15755876
-
Phosphorylation-acetylation switch in the regulation of STAT1 signaling.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010 Feb 5;315(1-2):40-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.10.007. Epub 2009 Oct 29. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 19879327 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Effects of FDA-Approved Multiple Sclerosis Drugs on Glial Cells and Neurons of the Central Nervous System.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 13;21(12):4229. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124229. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32545828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The lysine deacetylase inhibitor Givinostat inhibits β-cell IL-1β induced IL-1β transcription and processing.Islets. 2012 Nov-Dec;4(6):417-22. doi: 10.4161/isl.23541. Islets. 2012. PMID: 23486342 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of STAT signaling by acetylation.Cell Signal. 2013 Sep;25(9):1924-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.05.007. Epub 2013 May 22. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23707527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STAT1 signaling is not regulated by a phosphorylation-acetylation switch.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jul;31(14):3029-37. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05300-11. Epub 2011 May 16. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21576370 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Therapy Ties MYC Depletion to Reversing Immune Evasion and Treating Lung Cancer.Cell. 2017 Nov 30;171(6):1284-1300.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.022. Cell. 2017. PMID: 29195073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumann S., Dostert, A., Novac, N., Bauer, A., Schmid, W., Fas, S.C., Krueger, A., Heinzel, T., Kirchhoff, S., Schütz, G., et al. 2005. Glucocorticoids inhibit activation-induced cell death (AICD) via direct DNA-dependent repression of the CD95 ligand gene by a glucocorticoid receptor dimer. Blood 106: 617–625. - PubMed
-
- Baus D. and Pfitzner, E. 2005. Specific function of STAT3, SOCS1 and SOCS3 in the regulation of proliferation and survival of classical Hodgkin lymphoma cells. Int. J. Can. (Epub ahead of print October 4, 2005. PMID: 16206268] - PubMed
-
- Blobel G.A. 2000. CREB-binding protein and p300: Molecular integrators of hematopoietic transcription. Blood 95: 745–755. - PubMed
-
- Chen L.F. and Greene, W.C. 2003. Regulation of distinct biological activities of the NF-κB transcription factor complex by acetylation. J. Mol. Med. 81: 549–557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
