Reversion of severe hepatopulmonary syndrome in a non cirrhotic patient after corticosteroid treatment for granulomatous hepatitis: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 16482641
- PMCID: PMC4066050
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.336
Reversion of severe hepatopulmonary syndrome in a non cirrhotic patient after corticosteroid treatment for granulomatous hepatitis: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
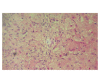
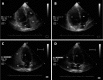
Hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) is defined as a clinical triad including liver disease, abnormal pulmonary gas exchange and evidence of intrapulmonary vascular dilatations. We report a 61-year-old male presented with fatigue, long-lasting fever, loss of weight, signs of portal hypertension, hepatosplenomegaly, cholestasis and progressive dyspnoea over the last year. Clinical, laboratory and histological findings confirmed the diagnosis of granulomatous hepatitis. HPS due to hepatic granuloma-induced portal hypertension was proved to be the cause of severe hypoxemia of the patient as confirmed by contrast-enhanced echocardiography. Reversion of HPS after corticosteroid therapy was confirmed by a new contrast-enhanced echocardiography along with the normalization of cholestatic enzymes and improvement of the patient's conditions. This is the first case of complete reversion of HPS in a non-cirrhotic patient with hepatic granuloma, indicating that intrapulmonary shunt in liver diseases is a functional phenomenon and HPS can be developed even in miscellaneous liver involvement as in this case.
Figures
References
-
- Hervé P, Lebrec D, Brenot F, Simonneau G, Humbert M, Sitbon O, Duroux P. Pulmonary vascular disorders in portal hypertension. Eur Respir J. 1998;11:1153–1166. - PubMed
-
- Naeije R. Hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension. Swiss Med Wkly. 2003;133:163–169. - PubMed
-
- Krowka MJ, Mandell MS, Ramsay MA, Kawut SM, Fallon MB, Manzarbeitia C, Pardo M, Marotta P, Uemoto S, Stoffel MP, et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension: a report of the multicenter liver transplant database. Liver Transpl. 2004;10:174–182. - PubMed
-
- Teuber G, Teupe C, Dietrich CF, Caspary WF, Buhl R, Zeuzem S. Pulmonary dysfunction in non-cirrhotic patients with chronic viral hepatitis. Eur J Intern Med. 2002;13:311–318. - PubMed
-
- Mimidis KP, Karatza C, Spiropoulos KV, Toulgaridis T, Charokopos NA, Thomopoulos KC, Margaritis VG, Nikolopoulou VN. Prevalence of intrapulmonary vascular dilatations in normoxaemic patients with early liver cirrhosis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998;33:988–992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

