Maternal care effects on the hippocampal transcriptome and anxiety-mediated behaviors in the offspring that are reversible in adulthood
- PMID: 16484373
- PMCID: PMC1413873
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507526103
Maternal care effects on the hippocampal transcriptome and anxiety-mediated behaviors in the offspring that are reversible in adulthood
Abstract
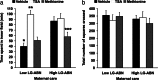
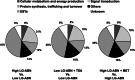
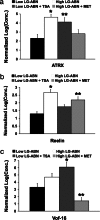
Early-life experience has long-term consequences on behavior and stress responsivity of the adult. We previously proposed that early-life experience results in stable epigenetic programming of glucocorticoid receptor gene expression in the hippocampus. The aim of this study was to examine the global effect of early-life experience on the hippocampal transcriptome and the development of stress-mediated behaviors in the offspring and whether such effects were reversible in adulthood. Adult offspring were centrally infused with saline vehicle, the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA), or the essential amino acid l-methionine. The animals were assessed in an unfamiliar open-field arena, and the hippocampal transcriptome of each animal was evaluated by microarray analysis. Here we report that TSA and methionine treatment reversed the effect of maternal care on open-field behavior. We identified >900 genes stably regulated by maternal care. A fraction of these differences in gene expression is reversible by either the histone deacetylase inhibitor TSA or the methyl donor l-methionine. These results suggest that early-life experience has a stable and broad effect on the hippocampal transcriptome and anxiety-mediated behavior, which is potentially reversible in adulthood.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

References
-
- Agrawal A. A. Science. 2001;294:321–326. - PubMed
-
- Meaney M. J. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001;24:1161–1192. - PubMed
-
- Liu D., Diorio J., Tannenbaum B., Caldji C., Francis D., Freedman A., Sharma S., Pearson D., Plotsky P. M., Meaney M. J. Science. 1997;277:1659–1662. - PubMed
-
- Francis D., Diorio J., Liu D., Meaney M. J. Science. 1999;286:1155–1158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

