Distribution characteristics, reproducibility, and precision of region of interest-based hippocampal diffusion tensor imaging measures
- PMID: 16484426
- PMCID: PMC8148767
Distribution characteristics, reproducibility, and precision of region of interest-based hippocampal diffusion tensor imaging measures
Abstract
Background and purpose: For adequate interpretation of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) parameters empirical distribution characteristics, precision, and reproducibility should be known. The present study investigated distribution and reliability parameters of hippocampal fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD).
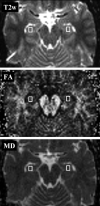
Methods: FA and MD values were averaged in hippocampal regions of interest in 20 subjects (10 women and 10 men; age range, 25-69 years). Regions of interest were manually placed bilaterally by one investigator at 2 occasions, and by a second independent investigator. Sample distributions of FA and MD values were compared with normal distributions. Intraclass coefficients (ICCs), standard errors of measurement (SEMs), and coefficients of variation (CVs) with confidence intervals (CI95s) were computed.
Results: The results did not show any deviation of averaged FA (0.237 +/- 0.017) and MD (775 +/- 28 microm2/s) values from normal distribution. Intraobserver reliability (ICC > or = 0.90) and precision (CV < or = 3.5%) were high for all measures. Interobserver reliability reached values of ICC > or = 0.84 and CV < or = 4.1%. FA yielded lower precision (CV 2.2-4.1%) than MD (CV 1.3-2.5%), CI95s were around +/-0.015-0.020 and +/-25-30 microm2/s for FA and MD, respectively. FA differences of 0.020-0.030 and MD differences of 40-50 microm2/s can be assumed to reflect reliably distinct values in hippocampal regions.
Conclusion: The results are in line with previous reports on reliability of DTI measures by using different designs and methodology. Notwithstanding the difficulties associated with region of interest-derived DTI measurements in hippocampal regions, the present approach provides estimates of distribution characteristics and precision applicable to routine assessments of DTI parameters in clinical and research context.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differences in Gaussian diffusion tensor imaging and non-Gaussian diffusion kurtosis imaging model-based estimates of diffusion tensor invariants in the human brain.Med Phys. 2016 May;43(5):2464. doi: 10.1118/1.4946819. Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 27147357
-
Region of interest correction factors improve reliability of diffusion imaging measures within and across scanners and field strengths.Neuroimage. 2015 Oct 1;119:406-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.06.078. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Neuroimage. 2015. PMID: 26146196 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the diagnostic performances of diffusion parameters in diffusion weighted imaging and diffusion tensor imaging of breast lesions.Eur J Radiol. 2013 Dec;82(12):e801-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 13. Eur J Radiol. 2013. PMID: 24099642
-
Multicenter Measurements of T1 Relaxation and Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Intra and Intersite Reproducibility.J Neuroimaging. 2019 Jan;29(1):42-51. doi: 10.1111/jon.12559. Epub 2018 Sep 19. J Neuroimaging. 2019. PMID: 30230638
-
The role of diffusion tensor imaging and fractional anisotropy in the evaluation of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a literature review.Neurosurg Focus. 2016 Sep;41(3):E12. doi: 10.3171/2016.6.FOCUS16192. Neurosurg Focus. 2016. PMID: 27581308 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultra-high resolution diffusion tensor imaging of the microscopic pathways of the medial temporal lobe.Neuroimage. 2012 Sep;62(3):2065-82. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.05.065. Epub 2012 Jun 5. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 22677150 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in microstructural alterations of the hippocampus in Alzheimer disease and idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a diffusion tensor imaging study.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010 Nov;31(10):1867-72. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2207. Epub 2010 Jul 29. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. PMID: 20671063 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diffusion imaging changes in grey matter in Alzheimer's disease: a potential marker of early neurodegeneration.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2015 Jul 1;7(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s13195-015-0132-3. eCollection 2015. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26136857 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion tensor imaging-based fractional anisotropy quantification in the corticospinal tract of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using a probabilistic mixture model.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007 Apr;28(4):724-30. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. PMID: 17416829 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability of the freehand region-of-interest method in quantitative cerebral diffusion tensor imaging.BMC Med Imaging. 2021 Oct 4;21(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12880-021-00663-8. BMC Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34607554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ramnani N, Behrens TE, Penny W, et al. New approaches for exploring anatomical and functional connectivity in the human brain. Biol Psychiatry 2004;56:613–19 - PubMed
-
- Loevner LA, Grossman RI, Cohen JA, et al. Microscopic disease in normal-appearing white matter on conventional MR images in patients with multiple sclerosis: assessment with magnetization-transfer measurements. Radiology 1995;96:511–15 - PubMed
-
- Tortorella C, Viti B, Bozzali M. A magnetization transfer histogram study of normal-appearing brain tissue in MS. Neurology 2000;54:186–93 - PubMed
-
- Fellgiebel A, Wille P, Müller MJ, et al. Ultrastructural hippocampal and white matter alterations in mild cognitive impairment: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2004;18:101–08 - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ, Pajevic S. A normal distribution for tensor-valued random variables: applications to diffusion tensor MRI. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2003;22:785–94 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
