Bax inhibition protects against free fatty acid-induced lysosomal permeabilization
- PMID: 16484678
- PMCID: PMC3056273
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00509.2005
Bax inhibition protects against free fatty acid-induced lysosomal permeabilization
Abstract
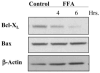
Lysosomal permeabilization is a key feature of hepatocyte lipotoxicity, yet the mechanisms mediating this critical cellular event are unclear. This study examined the mechanisms involved in free fatty acid (FFA)-induced lysosomal permeabilization and the role of Bax, a Bcl-2 family member, in this event. Exposure of liver cells to palmitate induced Bax activation and translocation to lysosomes. Studies to suppress Bax activation either by pharmacological approaches or small interfering-RNA-mediated inhibition of Bax expression showed that lysosomal permeabilization is Bax dependent. In addition, palmitate treatment resulted in a significant decrease in Bcl-X(L), a Bax antagonist. Moreover, forced Bcl-X(L) expression blocked lysosomal permeabilization. Lysosomal permeabilization by FFA was ceramide and caspase independent. Finally, paradigms that inhibit lysosomal permeabilization also reduced apoptosis. In conclusion, these data strongly support a regulatory role for Bax in FFA-mediated lysosomal permeabilization and subsequent cell death.
Figures
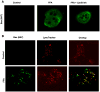
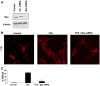
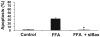
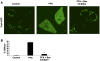

Similar articles
-
Methylmercury induces lysosomal membrane permeabilization through JNK-activated Bax lysosomal translocation in neuronal cells.Toxicol Lett. 2022 Mar 1;357:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2021.12.021. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Toxicol Lett. 2022. PMID: 34999165
-
BAX/MLKL signaling contributes to lipotoxicity-induced lysosomal membrane permeabilization in alcohol-associated liver disease.Autophagy. 2024 Apr;20(4):958-959. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2221989. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 37289043 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand activates a lysosomal pathway of apoptosis that is regulated by Bcl-2 proteins.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 28;282(39):28960-28970. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705671200. Epub 2007 Aug 8. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17686764
-
[Lysosomal membrane permeabilization as apoptogenic factor].Tsitologiia. 2011;53(4):313-24. Tsitologiia. 2011. PMID: 21675210 Review. Russian.
-
Lysosomal membrane permeabilization in cell death.Oncogene. 2008 Oct 27;27(50):6434-51. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.310. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18955971 Review.
Cited by
-
Coordination of mitochondrial and lysosomal homeostasis mitigates inflammation and muscle atrophy during aging.Aging Cell. 2022 Apr;21(4):e13583. doi: 10.1111/acel.13583. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Aging Cell. 2022. PMID: 35263007 Free PMC article.
-
Vegetable Oil-Peroxidation Product 'Hydroxynonenal' Causes Hepatocyte Injury and Steatosis via Hsp70.1 and BHMT Disorders in the Monkey Liver.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 14;15(8):1904. doi: 10.3390/nu15081904. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37111122 Free PMC article.
-
Lipids, lysosomes, and autophagy.J Lipid Res. 2016 Sep;57(9):1619-35. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R067520. Epub 2016 Jun 21. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 27330054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qushi Huayu Decoction Inhibits Hepatic Lipid Accumulation by Activating AMP-Activated Protein Kinase In Vivo and In Vitro.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:184358. doi: 10.1155/2013/184358. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23573117 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathways of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease development and progression.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Jan;76(1):99-128. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2947-0. Epub 2018 Oct 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30343320 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J, Sanderson SO, Lindor KD, Feldstein A, Angulo P. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:113–121. - PubMed
-
- Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1221–1231. - PubMed
-
- Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Pathology of steatohepatitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2002;16:691–707. - PubMed
-
- Clark JM, Brancati FL, Diehl AM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1649–1657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

