The vitamin D analogue BXL-628 inhibits growth factor-stimulated proliferation and invasion of DU145 prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 16485114
- PMCID: PMC12161086
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-006-0086-8
The vitamin D analogue BXL-628 inhibits growth factor-stimulated proliferation and invasion of DU145 prostate cancer cells
Abstract
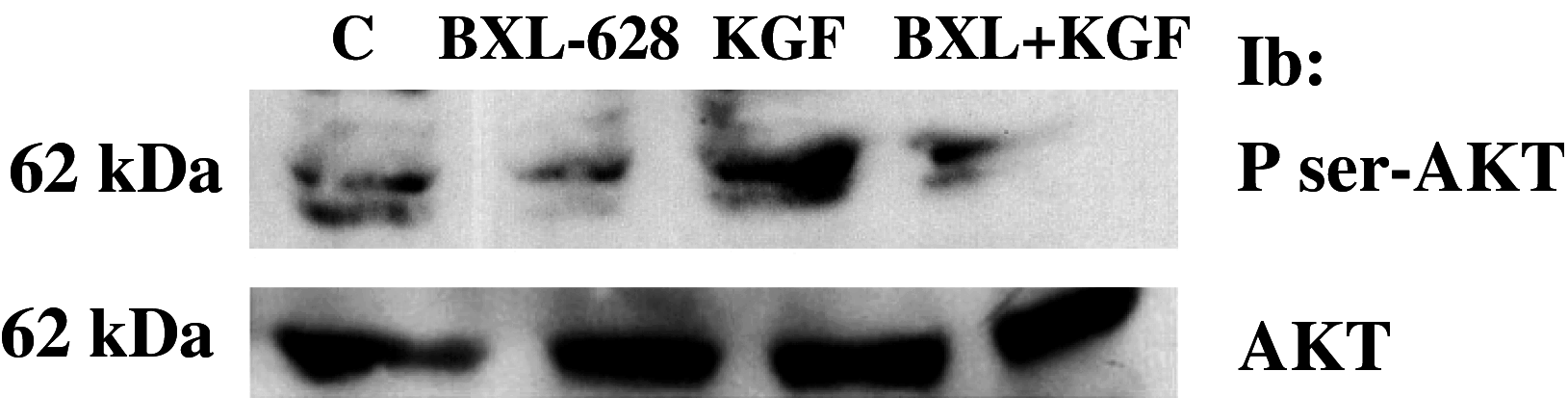
Purpose: Suppression of the invasive phenotype is essential in developing new therapeutic tools to treat advanced prostate cancer (PC) indicating that androgen-independent prostate cancer (AI-PC) is characterized by increased metastatic potential. In the present study, we have investigated the effect of the nonhypercalcemic vitamin D analogue BXL-628 on proliferation and invasive properties of the human PC cell line DU145. In particular, the effect of the analogue was tested following stimulation with a potent growth factor, keratinocyte growth factor (KGF), which stimulates both proliferation and invasion of these cells. We have also evaluated the effect of the analogue on KGF stimulation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
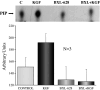
Methods: Cell proliferation was determined by cell counting. Invasion through Matrigel was evaluated using Boyden chambers. PI3K activity was measured by immunokinase assay and AKT phosphorylation was evaluated by western blot analysis. Keratinocyte growth factor receptor (KGFR) autotransphosphorylation was evaluated by western blot after immunoprecipitation of the receptor.
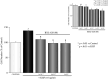
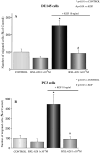
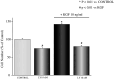
Results: BXL-628 is able to inhibit both proliferation and invasion of DU145 cells in basal conditions and in response to KGF. Following stimulation with KGF, the inhibition is due to suppression of KGFR autotransphosphorylation and downstream PI3K/AKT activation, both achieved following a brief (5 min) incubation with the analogue. This effect on KGFR autophosphorylation was still present when cells were treated with the alpha-amanitin, an inhibitor of RNA transcription, indicating a rapid, nongenomic effect.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that the vitamin D analogue BXL-628 is able to suppress KGF-induced proliferation and invasion of AI-PC cells in vitro, prospecting a possible use of the drug, which is currently in phase II clinical studies for benign prostatic hyperplasia, in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gefitinib ('IRESSA', ZD1839) inhibits EGF-induced invasion in prostate cancer cells by suppressing PI3 K/AKT activation.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004 Oct;130(10):604-14. doi: 10.1007/s00432-004-0581-8. Epub 2004 Jul 16. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15258753 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma via EGFR degradation.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21654. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05259-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594106 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-secreted KGF ameliorates acute lung injury via the Gab1/ERK/NF-κB signaling axis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jul 10;30(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00757-z. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40640718 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for preventing oral mucositis in patients with cancer receiving treatment: cytokines and growth factors.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 28;11(11):CD011990. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011990.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29181845 Free PMC article.
-
Non-genomic effects of the androgen receptor and vitamin D agonist are involved in suppressing invasive phenotype of prostate cancer cells.Steroids. 2006 Apr;71(4):304-9. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2005.09.010. Epub 2005 Nov 9. Steroids. 2006. PMID: 16289173 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of microRNA-98 as a therapeutic target inhibiting prostate cancer growth and a biomarker induced by vitamin D.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 4;288(1):1-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.395947. Epub 2012 Nov 27. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23188821 Free PMC article.
-
Testosterone insulin-like effects: an in vitro study on the short-term metabolic effects of testosterone in human skeletal muscle cells.J Endocrinol Invest. 2017 Oct;40(10):1133-1143. doi: 10.1007/s40618-017-0686-y. Epub 2017 May 15. J Endocrinol Invest. 2017. PMID: 28508346 Free PMC article.
-
Activated vitamin D3 and pro-activated vitamin D3 attenuate induction of permanent changes caused by neonatal estrogen exposure in the mouse vagina.J Reprod Dev. 2014;60(4):274-9. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2014-015. Epub 2014 Apr 25. J Reprod Dev. 2014. PMID: 24769840 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of testosterone and vitamin D analogue, elocalcitol, on insulin-controlled signal transduction pathway regulation in human skeletal muscle cells.J Endocrinol Invest. 2019 Aug;42(8):897-907. doi: 10.1007/s40618-018-0998-6. Epub 2019 Jan 1. J Endocrinol Invest. 2019. PMID: 30600434
-
The phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor tadalafil regulates lipidic homeostasis in human skeletal muscle cell metabolism.Endocrine. 2018 Mar;59(3):602-613. doi: 10.1007/s12020-017-1378-2. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Endocrine. 2018. PMID: 28786077
References
-
- Albini A, Iwamoto Y, Kleinman HK, Martin GR, Aaronson SA, Kozlowski JM, McEwan RN (1987) A rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of tumor cells. Cancer Res 47:3239–3245 - PubMed
-
- Baldi E, Bonaccorsi L, Forti G (2003) Androgen receptor: good guy or bad guy in prostate cancer invasion? Endocrinology 144:1653–1655 - PubMed
-
- Beer TM, Myrthue A, Eilers KM (2005) Rationale for the development and current status of calcitriol in androgen-independent prostate cancer. World J Urol 23:28–32 - PubMed
-
- Blay JY, Le Cesne A, Alberti L, Ray-Coquart I (2005) Targeted cancer therapies. Bull Cancer 92:E13–E18 - PubMed
-
- Bonaccorsi L, Luconi M, Maggi M, Muratori M, Forti G, Serio M, Baldi E (1997) Protein tyrosine kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase and protein kinase C are involved in the mitogenic signaling of platelet-activating factor (PAF) in HEC-1A cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1355:155–166 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

