Central African hunters exposed to simian immunodeficiency virus
- PMID: 16485481
- PMCID: PMC3367631
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1112.050394
Central African hunters exposed to simian immunodeficiency virus
Abstract
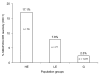
HIV-seronegative Cameroonians with exposure to nonhuman primates were tested for simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection. Seroreactivity was correlated with exposure risk (p<0.001). One person had strong humoral and weak cellular immune reactivity to SIVcol peptides. Humans are exposed to and possibly infected with SIV, which has major public health implications.
Figures

References
-
- Courgnaud V, Pourrut X, Bibollet-Ruche F, Mpoudi-Ngole E, Bourgeois A, Delaporte E, et al. Characterization of a novel simian immunodeficiency virus from guereza colobus monkeys (Colobus guereza) in Cameroon: a new lineage in the nonhuman primate lentivirus family. J Virol. 2001;75:857–66. 10.1128/JVI.75.2.857-866.2001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
