Hepatitis E virus transmission from wild boar meat
- PMID: 16485490
- PMCID: PMC3367655
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1112.051041
Hepatitis E virus transmission from wild boar meat
Abstract
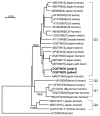
We investigated a case of hepatitis E acquired after persons ate wild boar meat. Genotype 3 hepatitis E virus (HEV) RNA was detected in both patient serum and wild boar meat. These findings provided direct evidence of zoonotic foodborne transmission of HEV from a wild boar to a human.
Figures
References
-
- Purcell RH, Emerson SU. Hepatitis E virus. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields virology. Fourth ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001. p. 3051–61.
-
- Emerson SU, Anderson D, Arankalle A, Meng XJ, Purdy M, Schlauder GG, et al. Hepevirus. In: Fauquet CM, Mayo MA, Maniloff J, Desselberger U, Ball LA, editors. Virus taxonomy: eighth report of the ICTV. London: Elsevier/Academic Press; 2004. p. 851–5.
-
- Meng X-J. Zoonotic and xenozoonotic risks of the hepatitis E virus. Infect Dis Rev. 2000;2:35–41.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
