CD127 expression and regulation are altered in the memory CD8 T cells of HIV-infected patients--reversal by highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART)
- PMID: 16487237
- PMCID: PMC1809599
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03022.x
CD127 expression and regulation are altered in the memory CD8 T cells of HIV-infected patients--reversal by highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART)
Abstract
HIV infection activates abnormally the immune system and the chronic phase is accompanied by marked alterations in the CD8 compartment. The expression of CD127 (IL-7R alpha chain) by memory CD8 T lymphocytes in HIV-infected patients is analysed and reported. The memory CD8 T cell subset was characterized by expression of CD45RA and CD27 markers, and CD127 cell surface expression was measured ex vivo by four-colour flow cytometry. HIV infection was associated with a fall in the proportion of CD127(+) cells among memory CD8 lymphocytes that resulted in a higher CD127(-) CD45RA(-)CD27(+) CD8 T cell count in HIV-infected patients. Diminished CD127 cell surface expression [mean fluorescence intensity (MFI)] by positive cells was also observed in this subset. The data suggest that these defects were reversed by highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART). The regulation of CD127 expression was also studied in vitro. Down-regulation of CD127 by interleukin (IL)-7 was observed in memory CD8 lymphocytes from healthy donors and HAART patients. Expression of CD127 by memory CD8 lymphocytes cultured in the absence of IL-7 confirmed that IL-7R regulation is altered in viraemic patients. Under the same experimental conditions, memory CD8 lymphocytes from HAART patients were shown to express CD127 at levels comparable to cells from healthy individuals. Altered CD127 cell surface expression and defective CD127 regulation in the memory CD8 T lymphocytes of HIV-infected patients are potential mechanisms by which these cells may be impeded in their physiological response to endogenous IL-7 stimulatory signals. Our data suggest that these defects are reversed during the immune reconstitution that follows HAART.
Figures
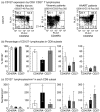
 , HAART patients. *P < 0·05 when compared to healthy donors; **P < 0·05 when compared to untreated viraemic patients.
, HAART patients. *P < 0·05 when compared to healthy donors; **P < 0·05 when compared to untreated viraemic patients.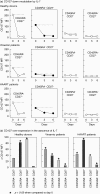
References
-
- Hazenberg MD, Otto SA, van Benthem BH, et al. Persistent immune activation in HIV-1 infection is associated with progression to AIDS. AIDS. 2003;17:1881–8. - PubMed
-
- Trimble LA, Lieberman J. Circulating CD8 T lymphocytes in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals have impaired function and downregulate CD3 zeta, the signaling chain of the T-cell receptor complex. Blood. 1998;91:585–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

