Development of serum IgM antibodies against superantigens of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes in Kawasaki disease
- PMID: 16487241
- PMCID: PMC1809617
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03015.x
Development of serum IgM antibodies against superantigens of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes in Kawasaki disease
Abstract
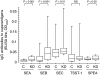
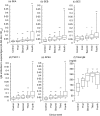
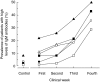
To serologically determine the association of microbial superantigens and the pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease (KD), we conducted a case-control study. Serum IgG and IgM antibodies against staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA), SEB, SEC, toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1), and streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A (SPEA) were measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 293 serum samples from 65 KD patients on clinical days 1-28 and 120 control samples. The administration of immunoglobulin products, which contain high concentrations of IgG antibodies against all the superantigens, directly elevated antitoxin IgG antibodies in KD patients. In contrast, antitoxin IgM antibodies were not detected in immunoglobulin products. Actually, we found a significant elevation of IgM antibodies against SEA in KD patients in the first (median titre: 0.020, P < 0.01 versus control), second (0.024, P < 0.001), third (0.030, P < 0.001) and fourth (0.038, P < 0.001) weeks, compared to the controls (0.015). Significant differences of IgM antibodies were also true for SEB, TSST-1, and SPEA throughout the first to fourth weeks, and for SEC throughout the second to fourth weeks. The prevalence of KD patients having high IgM titres (> mean + 2SD of control values) to the 5 superantigens was increased with the clinical weeks, and reached 29-43% of KD subjects at the fourth week. This is the first study that describes kinetics of IgM antibodies against superantigens and clarifies the serological significance throughout the clinical course of KD. Our results suggest that multiple superantigens involve in the pathogenesis of KD.
Figures
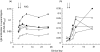
Similar articles
-
Antibodies to highly conserved peptide sequence of staphylococcal and streptococcal superantigens in Kawasaki disease.Exp Mol Pathol. 2004 Apr;76(2):117-21. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2003.12.003. Exp Mol Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15010289
-
Serologic evidence that streptococcal superantigens are not involved in the pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease.Microbiol Immunol. 1997;41(11):895-900. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1997.tb01947.x. Microbiol Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9444333
-
Possible relationship between streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A and Kawasaki syndrome in patients older than six months of age.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003 Sep;22(9):794-8. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000083824.15218.de. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003. PMID: 14506370
-
The role of superantigens of group A Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus in Kawasaki disease.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2007 Jun;20(3):298-303. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e3280964d8c. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17471041 Review.
-
Superantigens and pseudosuperantigens of gram-positive cocci.Med Microbiol Immunol. 1995 May;184(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/BF00216783. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1995. PMID: 8538573 Review.
Cited by
-
Kawasaki disease in siblings in close temporal proximity to each other-what are the implications?Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Mar;40(3):849-855. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05328-5. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 32776314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kawasaki disease: etiopathogenesis and novel treatment strategies.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017 Mar;13(3):247-258. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2017.1232165. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27590181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic dysfunction secondary to Kawasaki disease: characteristics, etiology and predictive role in coronary artery abnormalities.Clin Exp Med. 2020 Feb;20(1):21-30. doi: 10.1007/s10238-019-00596-1. Epub 2019 Nov 16. Clin Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 31734766
-
Adult-onset Kawasaki disease (mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome) and concurrent Coxsackievirus A4 infection: a case report.Int Med Case Rep J. 2015 Sep 29;8:225-30. doi: 10.2147/IMCRJ.S90685. eCollection 2015. Int Med Case Rep J. 2015. PMID: 26491373 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple roles of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins: pathogenicity, superantigenic activity, and correlation to antibiotic resistance.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Aug;2(8):2117-31. doi: 10.3390/toxins2082117. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burns JC, Glodé MP. Kawasaki syndrome. Lancet. 2004;364:533–44. - PubMed
-
- Japanese Kawasaki Disease Research Committee. Diagnostic Guidelines of Kawasaki Disease. 5. Tokyo: Japanese Kawasaki Disease Research Committee; 2002.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

