Tumour necrosis factor-alpha production stimulated by heat shock protein 70 and its inhibition in circulating dendritic cells and cells eluted from mucosal tissues in Crohn's disease
- PMID: 16487255
- PMCID: PMC1809607
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03010.x
Tumour necrosis factor-alpha production stimulated by heat shock protein 70 and its inhibition in circulating dendritic cells and cells eluted from mucosal tissues in Crohn's disease
Abstract
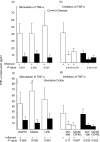
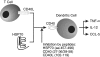
Summaryand interleukin (IL)-12 by dendritic cells (DC) from patients with Crohn's disease. TNF-alpha concentration was increased significantly when DC from Crohn's disease were stimulated with HSP70 or CD40L and this was associated with signalling by the extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 and p38 mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase pathway. IL-12 production was also increased when DC were stimulated with HSP70. Cells eluted from inflamed intestinal mucosa from Crohn's disease, stimulated with HSP70, CD40L or lipopolysaccharide produced significantly greater TNF-alpha and IL-12 concentrations than cells from uninflamed mucosa. Significant inhibition of TNF-alpha production was demonstrated when DC from peripheral blood mononuclear cells or cells eluted from intestinal mucosa of Crohn's disease were treated with either the HSP70 inhibitory peptide (aa 457-496) or peptides derived from CD40 and CD40L. These inhibitory peptides target the CD40-CD40L and the emerging CD40-HSP70 co-stimulatory pathway. Our findings offer a novel strategy to prevent excessive production of TNF-alpha in Crohn's disease.
Figures
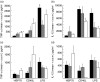
 (n = 9 and 8) and healthy controls ▪ (n = 13 and 14), respectively; statistical analyses were performed between CD and controls and UC and controls for each stimulant (*P < 0·05, **P < 0·02). Stimulation of monocytes in these groups producing (c) TNF-α (n = 10–16) and (d) IL-12 (n = 7–9), respectively.
(n = 9 and 8) and healthy controls ▪ (n = 13 and 14), respectively; statistical analyses were performed between CD and controls and UC and controls for each stimulant (*P < 0·05, **P < 0·02). Stimulation of monocytes in these groups producing (c) TNF-α (n = 10–16) and (d) IL-12 (n = 7–9), respectively.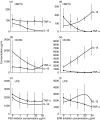
Similar articles
-
TNF-alpha blockade down-regulates the CD40/CD40L pathway in the mucosal microcirculation: a novel anti-inflammatory mechanism of infliximab in Crohn's disease.J Immunol. 2006 Feb 15;176(4):2617-24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.4.2617. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16456024 Clinical Trial.
-
NFAM1 Promotes Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Mouse and Human Monocytes.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 13;12:773445. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.773445. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095847 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperexpression of CD40 ligand (CD154) in inflammatory bowel disease and its contribution to pathogenic cytokine production.J Immunol. 1999 Oct 1;163(7):4049-57. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10491009
-
IL-1 and CD40/CD40L platelet complex: elements of induction of Crohn's disease and new therapeutic targets.Arch Pharm Res. 2021 Jan;44(1):117-132. doi: 10.1007/s12272-020-01296-1. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Arch Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 33394309 Review.
-
Inflammatory mediators in chronic inflammatory bowel diseases.Klin Wochenschr. 1991 Dec 15;69(21-23):981-7. doi: 10.1007/BF01645143. Klin Wochenschr. 1991. PMID: 1798295 Review.
Cited by
-
Securing the immune tightrope: mononuclear phagocytes in the intestinal lamina propria.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 Jun;10(6):415-26. doi: 10.1038/nri2778. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20498668 Review.
-
p38(MAPK): stress responses from molecular mechanisms to therapeutics.Trends Mol Med. 2009 Aug;15(8):369-79. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2009.06.005. Epub 2009 Aug 6. Trends Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19665431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heat shock protein-derived T-cell epitopes contribute to autoimmune inflammation in pediatric Crohn's disease.PLoS One. 2009 Nov 2;4(11):e7714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007714. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19888320 Free PMC article.
-
Saliva and Serum Cytokine Profiles During Oral Ulceration in Behçet's Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:724900. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.724900. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003055 Free PMC article.
-
Sinomenine hydrochloride improves DSS-induced colitis in mice through inhibition of the Notch signaling pathway.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):451. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03546-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39695403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duchmann R, Zeitz M. Crohn's disease. In: Ogra PL, Mestecky J, Lamm ME, Strober W, Bienenstock J, McGhee JR, editors. Mucosal immunology. San Diego: Academic Press; 2000. pp. 1055–80.
-
- Bouma G, Strober W. The immunological and genetic basis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:321–533. - PubMed
-
- Mathew CG, Lewis CM. Genetics of inflammatory bowel disease: progress and prospects. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13:161–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

