Characteristics of severe retinopathy of prematurity patients in China: a repeat of the first epidemic?
- PMID: 16488941
- PMCID: PMC1856940
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2005.078063
Characteristics of severe retinopathy of prematurity patients in China: a repeat of the first epidemic?
Abstract
Aim: To describe the characteristics of babies treated for severe retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) in a tertiary referral unit in China, to provide information to assist in determining screening criteria.
Methods: Information on consecutive babies referred to one eye department for treatment of stage 3 (prethreshold and threshold disease), and stages 4 and 5 ROP between January 2001 and May 2005 were retrieved from medical records.
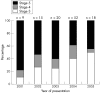
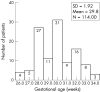
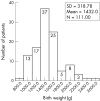
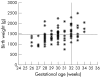
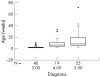
Results: Data from 114 babies were analysed. The number of babies treated increased from nine in 2001 to 52 in 2004. The numbers of infants in each stage of ROP were as follows: stage 3, 40 babies; stage 4, 19 babies, and stage 5, 55 cases. The mean gestational age (GA) was 29.8 (SD 1.9) weeks (range 26-34 weeks) and the mean birth weight (BW) was 1432 (319) g (range 760-2500 g). 31 babies had BWs more than 1500 g (27.2%). 10 cases (8.8%) had GAs more than 32 weeks, and 82 (71.9%) had GAs more than 28 weeks. Overall, 18 (16.2%) infants exceeded UK screening criteria, and 34 (30.4%) exceeded the criteria used in the United States. The median age at presentation was 5.5 months (range 1-72 months).
Conclusion: Comprehensive screening programmes for ROP are urgently needed in China. Screening criteria recommended by the American Academy of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus and the Royal College of Ophthalmologists, United Kingdom, may not be suitable for China where bigger, more mature babies are developing severe disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: none declared
Comment in
-
Retinopathy of prematurity.Br J Ophthalmol. 2006 Mar;90(3):254-5. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2005.081166. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006. PMID: 16488935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sorsby A.The incidence and causes of blindness in England and Wales 1948–1962. Reports on Public Health and Medical Subjects No 114. London: HMSO, 1966
-
- Doyle L W. Outcome to five years of age of children born at 24–26 weeks' GA in Victoria. Med J Aust 199516311–14. - PubMed
-
- King M. Retrolental fibroplasia. Arch Ophthalmol 195043695–709. - PubMed
-
- Hatfield E M. Blindness in infants and young children. Sight Sav Rev 19724269–89. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert C, Rahi J, Eckstein M.et al Retinopathy of prematurity in middle‐income countries. Lancet 199735012–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources