Optic disc size in a population based study in northern China: the Beijing Eye Study
- PMID: 16488961
- PMCID: PMC1856964
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2005.081521
Optic disc size in a population based study in northern China: the Beijing Eye Study
Abstract
Aim: To determine the optic disc size in the adult Chinese population in an urban and a rural region of Beijing.
Methods: The population based, cross sectional cohort study included 4439 subjects out of 5324 subjects invited to participate (response rate 83.4%). It was divided into a rural part (1973 (44.4%) subjects) and an urban part (2466 (55.6%) subjects). Mean age was 56.2 (SD 10.6) years (range 40-101 years). Colour optic disc photographs were morphometrically examined. Main outcome measure was optic disc area.
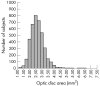
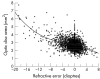
Results: Optic disc photographs were available for 4027 (90.7%) subjects. Mean optic disc area measured 2.65 (0.57) mm2 (range 1.03 mm2-7.75 mm2). Optic disc area was significantly (p<0.001) correlated with myopic refractive error, with a steep decrease in optic disc area from high myopia to the mid-range of refractive error, a slightly horizontal course in the refractive error range between -8 dioptres and +4 dioptres, and a further decrease in optic disc area towards higher hyperopia. Optic disc area was not related to age (p = 0.14) or sex (p = 0.93) (optic disc area, males: 2.65 (0.56) mm2 versus females: 2.65 (0.57) mm2). "Microdiscs" may be defined as smaller than 1.51 mm2, and "macrodiscs" as larger than 3.79 mm2.
Conclusions: Compared with data of preceding studies, mean optic disc size is larger in Chinese people than in white people. In Chinese people highly hyperopic eyes have significantly smaller optic discs, and highly myopic eyes have significantly larger optic discs than emmetropic eyes.
Conflict of interest statement
Proprietary interest: none.
References
-
- Franceschetti A, Bock R H. Megalopapilla: a new congenital anomaly. Am J Ophthalmol 195033227–235. - PubMed
-
- Bengtsson B. The variation and covariation of cup and disc diameters. Acta Ophthalmol 197654804–818. - PubMed
-
- Jonas J B, Gusek G C, Naumann G O H. Optic disc, cup and neuroretinal rim size, configuration, and correlations in normal eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988;29: 1151–8, Correction: Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1991321893 - PubMed
-
- Varma R, Tielsch J M, Quigley H A.et al Race‐, age‐, gender‐, and refractive error‐related differences in the normal optic disc. Arch Ophthalmol 19941121068–1076. - PubMed
-
- Ramrattan R S, Wolfs R C W, Hofmann A.et al Determinants of optic disk characteristics in a general population. The Rotterdam Study. Ophthalmology 19991061588–1596. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources