Protein S stimulates inhibition of the tissue factor pathway by tissue factor pathway inhibitor
- PMID: 16488980
- PMCID: PMC1413864
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0504240103
Protein S stimulates inhibition of the tissue factor pathway by tissue factor pathway inhibitor
Abstract
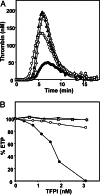
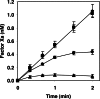
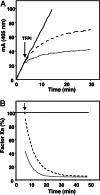
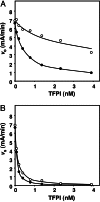
Tissue factor (TF) plays an important role in hemostasis, inflammation, angiogenesis, and the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis and cancer. In this article we uncover a mechanism in which protein S, which is well known as the cofactor of activated protein C, specifically inhibits TF activity by promoting the interaction between full-length TF pathway inhibitor (TFPI) and factor Xa (FXa). The stimulatory effect of protein S on FXa inhibition by TFPI is caused by a 10-fold reduction of the K(i) of the FXa/TFPI complex, which decreased from 4.4 nM in the absence of protein S to 0.5 nM in the presence of protein S. This decrease in K(i) not only results in an acceleration of the feedback inhibition of the TF-mediated coagulation pathway, but it also brings the TFPI concentration necessary for effective FXa inhibition well within range of the concentration of TFPI in plasma. This mechanism changes the concept of regulation of TF-induced thrombin formation in plasma and demonstrates that protein S and TFPI act in concert in the inhibition of TF activity. Our data suggest that protein S deficiency not only increases the risk of thrombosis by impairing the protein C system but also by reducing the ability of TFPI to down-regulate the extrinsic coagulation pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

