Bovine serum albumin antibodies as a disease marker for hepatitis E virus infection
- PMID: 16489265
- PMCID: PMC1361489
- DOI: 10.1155/JBB.2005.316
Bovine serum albumin antibodies as a disease marker for hepatitis E virus infection
Abstract
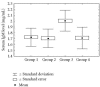
This report evaluates the significance of antibody/bovine serum albumin (BSA) interactions as a risk factor for the diagnosis of acute hepatitis E. Serum samples from 40 patients with acute hepatitis E and from 40 age/sex matched healthy adult subjects were tested for IgA, IgG, and IgM by ELISA and by turbidimetric assay. BSA was used as a target to characterize changes in levels of interacting immunoglobulins. Initial results obtained before removal of antibodies that interacted with BSA suggested that HEV patients had increased levels of IgM in their sera. It was found that normal individuals had mean IgA, IgG, and IgM levels of 2.55 mg/mL, 9.80 mg/mL, and 1.73 mg/mL, respectively while HEV patients had mean levels of 2.66 mg/mL, 10.04 mg/mL, and 2.01 mg/mL ($P < .26$ , $P < .32$, and $P < .0004$). However, the mean level of IgM in HEV-infected sera after purification from antibodies that interacted with BSA was determined to be 1.72 mg/mL indicating that there was no significant difference in IgM level in HEV patients compared to normal individuals ($P < .6$). The presence of antibodies that interact with BSA might serve as a diagnostic tool for detection of high-risk patients.
Figures

References
-
- Bradley D, Andjaparidze A, Cook E.H, Jr, et al. Aetiological agent of enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis. J Gen Virol. 1988;69(3):731–738. - PubMed
-
- Kane M.A, Bradley D.W, Shrestha S.M, et al. Epidemic non-A, non-B hepatitis in Nepal. Recovery of a possible etiologic agent and transmission studies in marmosets. JAMA. 1984;252(22):3140–3145. - PubMed
-
- Bryan J.P, Tsarev S.A, Iqbal M, et al. Epidemic hepatitis E in Pakistan: patterns of serologic response and evidence that antibody to hepatitis E virus protects against disease. J Infect Dis. 1994;170(3):517–521. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

