Known regulators of nitric oxide synthase and arginase are agonists at the human G-protein-coupled receptor GPRC6A
- PMID: 16491104
- PMCID: PMC1760712
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706682
Known regulators of nitric oxide synthase and arginase are agonists at the human G-protein-coupled receptor GPRC6A
Abstract
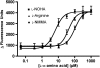
GPRC6A is a novel family C G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) with so far unknown physiological function. It was the aim of our study to further characterize the ligand preferences of the receptor and elucidate structural requirements for activity. We have previously generated a functional chimeric receptor construct, h6A/5.24, containing the ligand-binding amino-terminal domain of the human GPRC6A and the seven-transmembrane domain and carboxy terminus of the homologous goldfish receptor 5.24. Based on knowledge that this chimera prefers basic L-alpha-amino acids such as arginine, lysine and ornithine, we searched for commercially available analogues of these and other L-alpha-amino acids, and tested them for activity in a fluorescence-based calcium assay. The majority of the tested compounds are involved in the regulation of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and arginase enzymes. Altogether we profiled 30 different analogues. We found that a structurally wide range of L-alpha-amino-acid analogues of both arginine, lysine, and ornithine are agonists at h6A/5.24, whereas no antagonists were identified. From the profiling it is concluded that L-alpha-amino acids containing a highly basic side chain confer the highest activity, although the most potent compound was only twice as potent as L-arginine, which has a EC50 value of 23.5 microM. The reported agonism of NOS- and arginase-active compounds at GPRC6A has obvious implications in interpretation of experiments involving the NOS and arginase systems, and interfering effects at GPRC6A should be regarded of relevance, especially as the physiological function of the receptor is not yet understood.
Figures
Comment in
-
Common ligands of G-protein-coupled receptors and arginine-utilizing enzymes.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Apr;147(8):835-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706683. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16491103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BERTRAND H.O., BESSIS A.S., PIN J.P., ACHER F.C. Common and selective molecular determinants involved in metabotopic glutamate receptor agonist activity. J. Med. Chem. 2002;45:3171–3183. - PubMed
-
- BESSIS A.S., RONDARD P., GAVEN F., BRABET I., TRIBALLEAU N., PRÉZEAU L., ACHER F., PIN J.P. Closure of the Venus flytrap module of mGlu8 receptor and the activation process: insights from mutations converting antagonists into agonists. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2002;99:11097–11102. - PMC - PubMed
-
- BROWN E.M., GAMBA G., RICCARDI D., LOMBARDI M., BUTTERS R., KIFOR O., SUN A., HEDIGER M.A., LYTTON J., HEBERT S.C. Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature. 1993;366:575–580. - PubMed
-
- BRÄUNER-OSBORNE H., EGEBJERG J., NIELSEN E.Ø., MADSEN U., KROGSGAARD-LARSEN P. Ligands for glutamate receptors: design and therapeutic prospects. J. Med. Chem. 2000;43:2609–2645. - PubMed
-
- BUXTON I.L., CHEEK D.J., ECKMAN D., WESTFALL D.P., SANDERS K.M., KEEF K.D. NG-nitro L-arginine methyl ester and other alkyl esters of arginine are muscarinic receptor antagonists. Circ. Res. 1993;72:387–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

