ELEMENTAL SELENIUM GENERATED BY THE PHOTOBLEACHING OF SELENOMEROCYANINE PHOTOSENSITIZERS FORMS CONJUGATES WITH SERUM MACROMOLECULES THAT ARE TOXIC TO TUMOR CELLS
- PMID: 16491141
- PMCID: PMC1373681
- DOI: 10.1080/10426500590907200
ELEMENTAL SELENIUM GENERATED BY THE PHOTOBLEACHING OF SELENOMEROCYANINE PHOTOSENSITIZERS FORMS CONJUGATES WITH SERUM MACROMOLECULES THAT ARE TOXIC TO TUMOR CELLS
Abstract
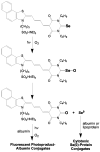
Elemental selenium generated by the photobleaching of selenomerocyanine dyes forms conjugates with serum albumin and serum lipoproteins that are toxic to leukemia and selected solid tumor cells but well tolerated by normal CD34-positive hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Serum albumin and lipoproteins act as Trojan horses that deliver the cytotoxic entity (elemental selenium) to tumor cells as part of a physiological process. They exploit the fact that many tumors have an increased demand for albumin and/or low-density lipoprotein. Se(0)-protein conjugates are more toxic than selenium dioxide, sodium selenite, selenomethionine, or selenocystine. They are only minimally affected by drug resistance mechanism, and they potentiate the cytotoxic effect of ionizing radiation and several standard chemotherapeutic agents. The cytotoxic mechanism of Se(0)-protein conjugates is not yet fully understood. Currently available data are consistent with the notion that Se(0)-protein conjugates act as air oxidation catalysts that cause a rapid depletion of intracellular glutathione and induce apoptosis. Drugs modeled after our Se(0)-protein conjugates may prove useful for the local and/or systemic therapy of cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Photochemically generated elemental selenium forms conjugates with serum proteins that are preferentially cytotoxic to leukemia and selected solid tumor cells.Photochem Photobiol. 2012 Mar-Apr;88(2):448-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2012.01078.x. Epub 2012 Jan 31. Photochem Photobiol. 2012. PMID: 22211823 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiated thyroid cancer and selenium supplements for protection of salivary glands from 131I treatment.Hell J Nucl Med. 2018 Jan-Apr;21(1):83-84. doi: 10.1967/s002449910712. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Hell J Nucl Med. 2018. PMID: 29550852
-
Biological potency of selenium from sodium selenite, selenomethionine, and selenocystine in the chick.Poult Sci. 1976 May;55(3):987-94. doi: 10.3382/ps.0550987. Poult Sci. 1976. PMID: 935062
-
[Progress in research of the product of the red elemental selenium reduced from selenium oxyanions by bacteria].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2007 Jun;47(3):554-7. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17672326 Review. Chinese.
-
Selenium: a double-edged sword for defense and offence in cancer.Arch Toxicol. 2010 Dec;84(12):919-38. doi: 10.1007/s00204-010-0595-8. Epub 2010 Sep 25. Arch Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20871980 Review.
Cited by
-
Ethyl 2-phenyl-3-(4-phenyl-1,2,3-selenadiazol-5-yl)-3-p-tolyl-propano-ate.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 Feb 1;68(Pt 2):o447. doi: 10.1107/S1600536811056017. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012. PMID: 22347058 Free PMC article.
-
Seleniranium ion-triggered reactions: new aspects of Friedel-Crafts and N-detosylative cyclizations.Org Lett. 2009 Jul 2;11(13):2924-7. doi: 10.1021/ol900961m. Org Lett. 2009. PMID: 19507847 Free PMC article.
-
5-[1-(4-Meth-oxy-phen-yl)-2-nitro-but-yl]-4-phenyl-1,2,3-selenadiazole.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 Jun 1;68(Pt 6):o1784. doi: 10.1107/S1600536812020752. Epub 2012 May 19. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012. PMID: 22719561 Free PMC article.
-
The chemistry of bisallenes.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2012;8:1936-98. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.8.225. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2012. PMID: 23209534 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and structural characterization of inverse-coordination clusters from a two-electron superatomic copper nanocluster.Chem Sci. 2018 Jul 2;9(33):6785-6795. doi: 10.1039/c8sc01508b. eCollection 2018 Sep 7. Chem Sci. 2018. PMID: 30310611 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Günther WHH, Searle R, Sieber F. Phosphorus Sulfur and Silicon. 1992;67:417.
-
- Günther WHH, Searle R, Sieber F. Sem. Hematol. 1992;29:88. - PubMed
-
- Krieg M, Bilitz JM, Traul DL, Sieber F. Cancer Res. Ther. Contr. 1995;4:163.
-
- Stehle G, Sinn H, Wunder A, Schrenk HH, Stewart JC, Hartung G, Maier-Borst W, Heene DL. Clin. Rev. Oncol.-Hemat. 1997;26:77. - PubMed
-
- Stehle G, Wunder A, Schrenk HH, Hartung G, Heene DL, Sinn H. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 1999;10:785. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources