Disease caused by non-tuberculous mycobacteria in a university hospital in Taiwan, 1997-2003
- PMID: 16492317
- PMCID: PMC2870472
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268805005698
Disease caused by non-tuberculous mycobacteria in a university hospital in Taiwan, 1997-2003
Abstract
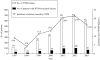
From January 1997 to December 2003, all patients with non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) isolation who were treated at a university hospital in Taiwan were evaluated. Among the 2650 NTM isolates, 1225 (46.2%) were from 412 patients with clinically significant diseases. The annual incidence (per 100000 patients) of disease caused by NTM was 8.96 in 1997, 21.53 in 2002, and 16.55 in 2003. The major types of infections caused by NTM included isolated pulmonary infection and pleurisy (59.5%), skin/soft-tissue infections and osteomyelitis (13.8%), and disseminated diseases (13.3%). The two most common groups of organisms involved were rapidly growing mycobacteria (RGM) (41.4%) and Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) (39%). The most common organism involved in isolated pulmonary infection and pleurisy was MAC (44.1%). RGM predominated in keratitis (94%), skin/soft-tissue infections and osteomyelitis (43.9%), and lymphadenitis (66.7%). This retrospective 7-year study demonstrated an increase in the incidence of NTM disease in a university hospital.
Figures

References
-
- Lewis AG et al. A clinical study of the chronic lung disease due to nonphotochromogenic acid-fast bacilli. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1960;53:273–285. - PubMed
-
- Wolinsky E. Nontuberculous mycobacteria and associated diseases. American Review of Respiratory Disease. 1979;119:107–159. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society. Diagnosis and treatment of disease caused by nontuberculous mycobacteria. American Review of Respiratory Disease. 1990;142:940–953. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society. Diagnosis and treatment of disease caused by nontuberculous mycobacteria. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 1997;156:S1–25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

