Synergistic roles of Mdm2 and Mdm4 for p53 inhibition in central nervous system development
- PMID: 16492743
- PMCID: PMC1413885
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508500103
Synergistic roles of Mdm2 and Mdm4 for p53 inhibition in central nervous system development
Abstract
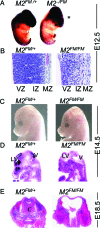
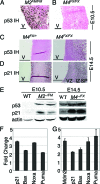
Loss of Mdm2 or Mdm4 leads to embryo lethal phenotypes that are p53-dependent. To determine whether Mdm2 and Mdm4 inhibit p53 function redundantly in a more restricted cell type, conditional alleles were crossed to a neuronal specific Cre transgene to delete Mdm2 and Mdm4 in the CNS. Mice lacking Mdm2 in the CNS developed hydranencephaly at embryonic day 12.5 due to apoptosis, whereas Mdm4 deletion showed a proencephaly phenotype at embryonic day 17.5 because of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. The deletion of both genes, strikingly, contributed to an even earlier and more severe CNS phenotype. Additionally, Mdm2 and Mdm4 had a gene dosage effect, because loss of three of the four Mdm alleles also showed a more accelerated CNS phenotype than deletion of either gene alone. All phenotypes were rescued by deletion of p53. Thus, these in vivo data demonstrate the importance of Mdm4 independent of Mdm2 in inhibition of p53.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mdm4 and Mdm2 cooperate to inhibit p53 activity in proliferating and quiescent cells in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Feb 28;103(9):3232-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508476103. Epub 2006 Feb 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16492744 Free PMC article.
-
A mouse p53 mutant lacking the proline-rich domain rescues Mdm4 deficiency and provides insight into the Mdm2-Mdm4-p53 regulatory network.Cancer Cell. 2006 Apr;9(4):273-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.03.014. Cancer Cell. 2006. PMID: 16616333
-
Tissue-specific differences of p53 inhibition by Mdm2 and Mdm4.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jan;26(1):192-8. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.192-198.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16354690 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of Mdm2 and Mdm4 and their clinical implications.Chin J Cancer. 2013 Jul;32(7):371-5. doi: 10.5732/cjc.012.10286. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Chin J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23327795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keeping p53 in check: essential and synergistic functions of Mdm2 and Mdm4.Cell Death Differ. 2006 Jun;13(6):927-34. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401912. Cell Death Differ. 2006. PMID: 16543935 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Regulation of p53: a collaboration between Mdm2 and Mdmx.Oncotarget. 2012 Mar;3(3):228-35. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.443. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 22410433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using Mouse Models to Explore MDM-p53 Signaling in Development, Cell Growth, and Tumorigenesis.Genes Cancer. 2012 Mar;3(3-4):209-18. doi: 10.1177/1947601912455324. Genes Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23150754 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation analysis of the MDM4 gene in German breast cancer patients.BMC Cancer. 2008 Feb 15;8:52. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-8-52. BMC Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18279506 Free PMC article.
-
Tau protein binds to the P53 E3 ubiquitin ligase MDM2.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 23;13(1):10208. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37046-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37353565 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of p53 stabilization by ATM after DNA damage.Cell Cycle. 2010 Feb 1;9(3):472-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.3.10556. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20081365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vousden K. H., Prives C. Cell. 2005;120:7–10. - PubMed
-
- Hollstein M., Hergenhahn M., Yang Q., Bartsch H., Wang Z. Q., Hainaut P. Mutat. Res. 1999;431:199–209. - PubMed
-
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. Cell. 1992;69:1237–1245. - PubMed
-
- Leng R. P., Lin Y., Ma W., Wu H., Lemmers B., Chung S., Parant J. M., Lozano G., Hakem R., Benchimol S. Cell. 2003;112:779–791. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

