AMPA receptor downscaling at the onset of Alzheimer's disease pathology in double knockin mice
- PMID: 16492745
- PMCID: PMC1413872
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507313103
AMPA receptor downscaling at the onset of Alzheimer's disease pathology in double knockin mice
Abstract
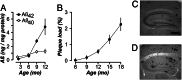
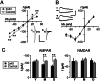
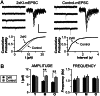
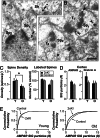
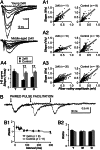
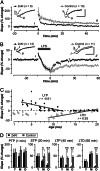
It is widely thought that Alzheimer's disease (AD) begins as a malfunction of synapses, eventually leading to cognitive impairment and dementia. Homeostatic synaptic scaling is a mechanism that could be crucial at the onset of AD but has not been examined experimentally. In this process, the synaptic strength of a neuron is modified so that the overall excitability of the cell is maintained. Here, we investigate whether synaptic scaling mediated by l-alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPARs) contributes to pathology in double knockin (2 x KI) mice carrying human mutations in the genes for amyloid precursor protein and presenilin-1. By using whole-cell recordings, we show that 2 x KI mice exhibit age-related downscaling of AMPAR-mediated evoked currents and spontaneous, miniature currents. Electron microscopic analysis further corroborates the synaptic AMPAR decrease. Additionally, 2 x KI mice show age-related deficits in bidirectional plasticity (long-term potentiation and long-term depression) and memory flexibility. These results suggest that AMPARs are important synaptic targets for AD and provide evidence that cognitive impairment may involve downscaling of postsynaptic AMPAR function.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

