RNA polymerase II subunit Rpb9 is important for transcriptional fidelity in vivo
- PMID: 16492753
- PMCID: PMC1413937
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0511330103
RNA polymerase II subunit Rpb9 is important for transcriptional fidelity in vivo
Abstract
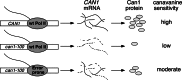
The fidelity of yeast RNA polymerase II (Pol II) was assessed in vivo with an assay in which errors in transcription of can1-100, a nonsense allele of CAN1, result in enhanced sensitivity to the toxic arginine analog canavanine. The Pol II accessory factor TFIIS has been proposed to play a role in transcript editing by stimulating the intrinsic nuclease activity of the RNA polymerase. However, deletion of DST1, the gene encoding the yeast homolog of TFIIS, had only a small effect on transcriptional fidelity, as determined by this assay. In contrast, strains containing a deletion of RPB9, which encodes a small core subunit of Pol II, were found to engage in error-prone transcription. rpb9Delta strains also had increased steady-state levels of can1-100 mRNA, consistent with transcriptional errors that decrease the normal sensitivity of the can1-100 transcript to nonsense-mediated decay, a pathway that degrades mRNAs with premature stop codons. Sequences of cDNAs from rpb9Delta strains confirmed a significantly increased occurrence of transcriptional substitutions and insertions. These results suggest that Rpb9 plays an important role in maintaining transcriptional fidelity, whereas TFIIS may serve a different primary purpose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Stimulation of RNA polymerase II transcript cleavage activity contributes to maintain transcriptional fidelity in yeast.Genes Cells. 2007 May;12(5):547-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2007.01072.x. Genes Cells. 2007. PMID: 17535246
-
Fidelity of RNA polymerase II transcription: Role of Rpb9 [corrected] in error detection and proofreading.Biochemistry. 2013 Nov 5;52(44):7807-17. doi: 10.1021/bi4009566. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 24099331
-
Members of the SAGA and Mediator complexes are partners of the transcription elongation factor TFIIS.EMBO J. 2004 Oct 27;23(21):4232-42. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600326. Epub 2004 Sep 9. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15359273 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II structure: from core to functional complexes.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004 Apr;14(2):218-26. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2004.01.003. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004. PMID: 15196470 Review.
-
Isolation and characterization of transcription fidelity mutants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jul;1819(7):694-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.02.005. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22366339 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure and function of the Si3 insertion integrated into the trigger loop/helix of cyanobacterial RNA polymerase.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 11:2024.01.11.575193. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.11.575193. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 20;121(8):e2311480121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2311480121. PMID: 38260627 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Evidence that the transcription elongation function of Rpb9 is involved in transcription-coupled DNA repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;26(24):9430-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01656-06. Epub 2006 Oct 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17030604 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-deep sequencing reveals pre-mRNA splicing as a sequence driven high-fidelity process.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 3;14(10):e0223132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223132. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31581208 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors that influence RNA polymerases I and II: To what extent is mechanism of action conserved?Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017 Feb;1860(2):246-255. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.10.010. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017. PMID: 27989933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA polymerase errors cause splicing defects and can be regulated by differential expression of RNA polymerase subunits.Elife. 2015 Dec 10;4:e09945. doi: 10.7554/eLife.09945. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26652005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shcherbakova P. V., Pavlov Y. I., Chilkova O., Rogozin I. B., Johansson E., Kunkel T. A. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:43770–43780. - PubMed
-
- Fish R. N., Kane C. M. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2002;1577:287–307. - PubMed
-
- Kettenberger H., Armache K.-J., Cramer P. Cell. 2003;114:347–357. - PubMed
-
- Opalka N., Chlenov M., Chacon P., Rice W. J., Wriggers W., Darst S. A. Cell. 2003;114:335–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

