Mutant huntingtin: nuclear translocation and cytotoxicity mediated by GAPDH
- PMID: 16492755
- PMCID: PMC1413934
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0511316103
Mutant huntingtin: nuclear translocation and cytotoxicity mediated by GAPDH
Abstract
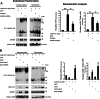
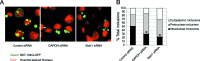
The pathophysiology of Huntington's disease reflects actions of mutant Huntingtin (Htt) (mHtt) protein with polyglutamine repeats, whose N-terminal fragment translocates to the nucleus to elicit neurotoxicity. We establish that the nuclear translocation and associated cytotoxicity of mHtt reflect a ternary complex of mHtt with GAPDH and Siah1, a ubiquitin-E3-ligase. Overexpression of GAPDH or Siah1 enhances nuclear translocation of mHtt and cytotoxicity, whereas GAPDH mutants that cannot bind Siah1 prevent translocation. Depletion of GAPDH or Siah1 by RNA interference diminishes nuclear translocation of mHtt.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
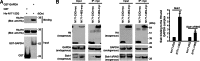
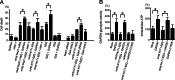
References
-
- The Huntington’s Disease Collaborative Research Group. Cell. 1993;72:971–983. - PubMed
-
- Peters M. F., Nucifora F. C., Jr., Kushi J., Seaman H. C., Cooper J. K., Herring W. J., Dawson V. L., Dawson T. M., Ross C. A. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1999;14:121–128. - PubMed
-
- Saudou F., Finkbeiner S., Devys D., Greenberg M. E. Cell. 1998;95:55–66. - PubMed
-
- Hodgson J. G., Agopyan N., Gutekunst C. A., Leavitt B. R., LePiane F., Singaraja R., Smith D. J., Bissada N., McCutcheon K., Nasir J., et al. Neuron. 1999;23:181–192. - PubMed
-
- Wheeler V. C., White J. K., Gutekunst C. A., Vrbanac V., Weaver M., Li X. J., Li S. H., Yi H., Vonsattel J. P., Gusella J. F., et al. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000;9:503–513. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

