Rhodopsin self-associates in asolectin liposomes
- PMID: 16492772
- PMCID: PMC1413906
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0511010103
Rhodopsin self-associates in asolectin liposomes
Abstract
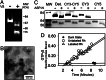
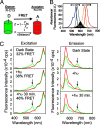
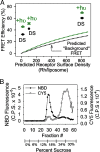
We show that the photoreceptor rhodopsin (Rh) can exist in the membrane as a dimer or multimer using luminescence resonance energy transfer and FRET methods. Our approach looked for interactions between Rh molecules reconstituted into asolectin liposomes. The low receptor density used in the measurements ensured minimal receptor crowding and artifactual association. The fluorescently labeled Rh molecules were fully functional, as measured by their ability to activate the G protein transducin. The luminescence resonance energy transfer measurements revealed a distance of 47-50 Angstroms between Rh molecules. The measured efficiency of FRET between receptors was close to the theoretical maximum possible, indicating nearly quantitative Rh-Rh association. Together, these results provide compelling evidence that Rh spontaneously self-associates in membranes.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rhodopsin/transducin interactions. I. Characterization of the binding of the transducin-beta gamma subunit complex to rhodopsin using fluorescence spectroscopy.J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17032-9. J Biol Chem. 1992. PMID: 1512242
-
Interaction of transducin with light-activated rhodopsin protects It from proteolytic digestion by trypsin.J Biol Chem. 1996 Nov 22;271(47):30034-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.47.30034. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8939950
-
Monomeric rhodopsin is sufficient for normal rhodopsin kinase (GRK1) phosphorylation and arrestin-1 binding.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 14;286(2):1420-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.151043. Epub 2010 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 20966068 Free PMC article.
-
Intramolecular interactions that induce helical rearrangement upon rhodopsin activation: light-induced structural changes in metarhodopsin IIa probed by cysteine S-H stretching vibrations.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 16;289(20):13792-800. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.527606. Epub 2014 Apr 1. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24692562 Free PMC article.
-
A physiological role for the supramolecular organization of rhodopsin and transducin in rod photoreceptors.FEBS Lett. 2013 Jun 27;587(13):2060-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.05.017. Epub 2013 May 16. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 23684654 Review.
Cited by
-
Autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa and E150K mutation in the opsin gene.J Biol Chem. 2006 Aug 4;281(31):22289-22298. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602664200. Epub 2006 May 31. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16737970 Free PMC article.
-
Distance mapping in proteins using fluorescence spectroscopy: the tryptophan-induced quenching (TrIQ) method.Biochemistry. 2010 Nov 16;49(45):9722-31. doi: 10.1021/bi100907m. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20886836 Free PMC article.
-
Each rhodopsin molecule binds its own arrestin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 27;104(9):3125-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610886104. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17360618 Free PMC article.
-
Time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy measures clustering and mobility of a G protein-coupled receptor opsin in live cell membranes.J Am Chem Soc. 2014 Jun 11;136(23):8342-9. doi: 10.1021/ja501948w. Epub 2014 Jun 2. J Am Chem Soc. 2014. PMID: 24831851 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and structural characterization of rhodopsin oligomers.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 28;281(17):11917-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600422200. Epub 2006 Feb 22. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16495215 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

