Opsin is present as dimers in COS1 cells: identification of amino acids at the dimeric interface
- PMID: 16492774
- PMCID: PMC1413904
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0510982103
Opsin is present as dimers in COS1 cells: identification of amino acids at the dimeric interface
Abstract
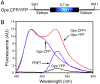
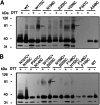
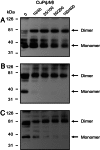
Rhodopsin in the disk membranes of rod outer segments serves as the dim-light photoreceptor and is a prototypic member of a G protein-coupled receptor family. Electron and atomic-force microscopy indicate that rhodopsin is present as dimers in the native membranes. Here, we have expressed the protein, opsin, in COS1 cells and have studied its molecular state by using FRET and by intermolecular cross-linking after site-directed cysteine mutagenesis. To observe FRET, the ends of the genes corresponding to the N termini of the cyan or yellow fluorescent proteins were fused to the ends of the genes corresponding to the C terminus of the opsin and the resulting fused genes were expressed in COS1 cells. The emission spectra in situ of the expressed proteins were recorded, and FRET was then calculated. The result indicated intermolecular interaction between opsin molecules in COS1 cells. To identify the amino acids involved in the interaction, those predicted by molecular modeling to be at the dimer interface were mutated one at a time to cysteine, and dimer formation was measured by the rate of disulfide bond formation in the presence of cupric orthophenanthroline. The mutants W175C and Y206C formed the dimers most rapidly, showing that the two amino acids were at the dimer interface.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Calorimetric studies of bovine rod outer segment disk membranes support a monomeric unit for both rhodopsin and opsin.Biophys J. 2008 Sep 15;95(6):2859-66. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.108.128868. Epub 2008 Jun 27. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18586850 Free PMC article.
-
State-dependent disulfide cross-linking in rhodopsin.Biochemistry. 1999 Sep 14;38(37):12028-32. doi: 10.1021/bi990948+. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10508406
-
Organization of the G protein-coupled receptors rhodopsin and opsin in native membranes.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 13;278(24):21655-21662. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302536200. Epub 2003 Mar 27. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12663652 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of amino acids at two dimer interface regions of the alpha-factor receptor (Ste2).Biochemistry. 2009 Aug 4;48(30):7132-9. doi: 10.1021/bi900424h. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19588927
-
The opsins.Genome Biol. 2005;6(3):213. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-3-213. Epub 2005 Mar 1. Genome Biol. 2005. PMID: 15774036 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quaternary structures of opsin in live cells revealed by FRET spectrometry.Biochem J. 2016 Nov 1;473(21):3819-3836. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160422. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27623775 Free PMC article.
-
Role of membrane integrity on G protein-coupled receptors: Rhodopsin stability and function.Prog Lipid Res. 2011 Jul;50(3):267-77. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2011.03.002. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Prog Lipid Res. 2011. PMID: 21435354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monomeric G protein-coupled receptor rhodopsin in solution activates its G protein transducin at the diffusion limit.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jun 26;104(26):10859-64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701967104. Epub 2007 Jun 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17578920 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodopsin self-associates in asolectin liposomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Feb 28;103(9):3060-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511010103. Epub 2006 Feb 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16492772 Free PMC article.
-
Misfolded opsin mutants display elevated β-sheet structure.FEBS Lett. 2015 Oct 7;589(20 Pt B):3119-25. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.08.042. Epub 2015 Sep 7. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 26358292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouvier M. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001;2:274–286. - PubMed
-
- Palczewski K., Kumasaka T., Hori T., Behnke C. A., Motoshima H., Fox B. A., LeTrong I., Teller D. C., Okada T., Stenkamp R. E., et al. Science. 2000;289:739–745. - PubMed
-
- White J. H., Wise A., Main M. J., Green A., Fraser N. J., Disney G. H., Barnes A. A., Emson P., Foord S. M., Marshall F. H. Nature. 1998;396:679–682. - PubMed
-
- Nelson G., Hoon M. A., Chandrasekhar J., Zhang Y., Ryba N. J. P., Zuker C. S. Cell. 2001;106:381–390. - PubMed
-
- George S.R., O’Dowd B. F., Lee S. P. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002;1:808–820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

