The Vif and Vpr accessory proteins independently cause HIV-1-induced T cell cytopathicity and cell cycle arrest
- PMID: 16492778
- PMCID: PMC1413893
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0509417103
The Vif and Vpr accessory proteins independently cause HIV-1-induced T cell cytopathicity and cell cycle arrest
Abstract
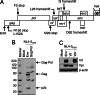
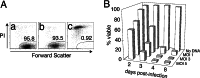
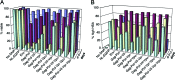
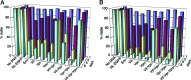
HIV type I (HIV-1) can cause G(2) cell cycle arrest and death of CD4(+) T lymphocytes in vitro and inexorable depletion of these cells in vivo. However, the molecular mechanism of viral cytopathicity has not been satisfactorily elucidated. Previously, we showed that HIV-1 kills T cells by a necrotic form of cell death that requires high level expression of an integrated provirus but not the env or nef genes. To determine which viral protein(s) are required for cell death, we systematically mutated, alone and in combination, the ORFs of the NL4-3 strain of HIV-1. We found that the elimination of the viral functions encoded by gag-pol and vpu, tat, and rev did not mitigate cytopathicity. However, elimination of the vif and vpr accessory genes together, but not individually, renders the virus incapable of causing cell death and G(2) cell cycle blockade. We thus identify vif and vpr as necessary for T cell cytopathic effects induced by HIV-1. These findings may provide an important insight into the molecular mechanism of viral pathogenesis in AIDS.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

References
-
- Gallo R. C. Immunol. Rev. 2002;185:236–265. - PubMed
-
- Ho D. D., Neumann A. U., Perelson A. S., Chen W., Leonard J. M., Markowitz M. Nature. 1995;373:123–126. - PubMed
-
- Perelson A. S., Neumann A. U., Markowitz M., Leonard J. M., Ho D. D. Science. 1996;271:1582–1586. - PubMed
-
- Wei X., Ghosh S. K., Taylor M. E., Johnson V. A., Emini E. A., Deutsch P., Lifson J. D., Bonhoeffer S., Nowak M. A., Hahn B. H., et al. Nature. 1995;373:117–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

